J Nucl Med 1995 Jun;36(6):969-74
Age and gender differences in normal myocardial adrenergic neuronal function
evaluated by iodine-123-MIBG imaging.
Tsuchimochi S, Tamaki N, Tadamura E, Kawamoto M, Fujita T, Yonekura Y, Konishi
J.
Myocardial sympathetic nervous function has been evaluated with
123I-metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) imaging in various cardiac diseases.
Heterogeneous distribution of this tracer has been reported. This study was
undertaken to assess whether such heterogeneity is related to age and gender.
METHODS: Twenty-nine subjects (18 men, 11 women; age range, 21 to 79 yr; mean
age 42 +/- 17 yr) with no cardiac disorders were studied. Early (15 min) and
late (3-4 hr) planar images were taken, and SPECT images were also obtained 3-4
hr after MIBG injection (111 MBq). The mean counts of the whole heart,
mediastinum and the anterior and inferior regions of the heart were obtained to
calculate heart-to-mediastinum count ratios, myocardial washout rates and the
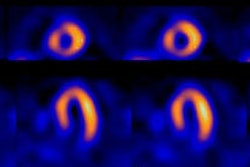
inferior-to-anterior wall count ratio. On a bull's-eye map of the SPECT images,
the left ventricular myocardium was divided into nine sectors to calculate the
inferior-to-anterior wall count ratio. RESULTS: There were no significant
differences in the heart-to-mediastinum count ratio based on age or gender, but
there was a significant inverse correlation between the inferior-to-anterior
wall count ratio and age (r = -0.51 on late planar images and r = -0.69 on SPECT;
p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively). This correlation was valid in men
(r = -0.74 and -0.83, respectively; both p < 0.001), but not in women (r =
-0.25 and -0.34, respectively; p = ns). CONCLUSION: Inferior wall uptake of MIBG
decreased with age in individuals without cardiac diseases, especially men. Such
age- and gender-related heterogeneity should be considered in the interpretation
of MIBG images.