Image of the Year
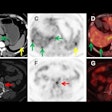
Minnies 2024 Winner: Diffusion tensor imaging (3T, 32 encoding directions, b=800 s/mm, 2mm isotropic resolution) reveals that high levels of soccer heading over two years is associated with changes in brain microstructure similar to findings seen in mild traumatic brain injury. Image from Michael Lipton, MD, PhD, of Columbia University, et al.
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an advanced MRI technique that detects white matter fibers that connect different parts of the brain by tracking the microscopic movement of water molecules through the tissue. In a study first presented at RSNA last year, DTI linked soccer heading to a decline in the microstructure and function of the brain in soccer players over two years.
“Quantitative measures derived using the diffusion measurement were employed in our study to identify subtle but important disruption of brain structure caused by soccer heading," Michael Lipton, MD, PhD, senior author and head of Columbia University’s Translational Neuroimaging Laboratory, told AuntMinnie.com.
 Researchers used diffusion tensor imaging to study the impact of soccer heading on the brain. This method tracks the microscopic movement of water molecules through brain tissue to characterize the brain's microstructure. Image courtesy of Michael Lipton, MD, PhD.
Researchers used diffusion tensor imaging to study the impact of soccer heading on the brain. This method tracks the microscopic movement of water molecules through brain tissue to characterize the brain's microstructure. Image courtesy of Michael Lipton, MD, PhD.
The study included 148 young adult amateur soccer players (mean age 27, 26% women). The players underwent DTI, neurite orientation dispersion, and density imaging, as well as a set of neurocognitive tests to assess brain function, at their initial visits and two years later. Two-year heading exposure was categorized as low (0-556 total headers), moderate (564-1,512 total headers), or high (1,538-23,462 total headers) using a questionnaire.
Compared to the baseline test results, the high-heading group demonstrated a loss or disruption in tissue structure, characterized by an increase of mean diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and axial diffusivity in frontal white matter regions. Imaging also detected a decrease of orientation-dispersion index (a measure of brain organization) in the right superior frontal white matter and superior corona radiata.
In addition, high levels of heading were also associated with a decline in verbal learning performance on a memory test. In contrast, participants who engaged in low or no heading demonstrated decreases in diffusivity and improvement in verbal learning performance, according to the group.
"This is an example of the elegant delineation of white matter anatomy that can be achieved in vivo using diffusion tensor imaging. The colored lines reflect the direction of water diffusion within brain tissue, which is constrained by the microscopic structure of axon bundles comprising white matter tracts. This image displays the corticospinal fibers as they course through the deep cerebral white matter and internal capsule toward the brainstem," Lipton said.
Ultimately, the results are suggestive of a subclinical effect, given the subsignificant pattern of verbal learning changes, the researchers noted.
"This is the first study to show a change of brain structure over the long term related to subconcussive head impacts in soccer,” Lipton noted.
Larger longitudinal studies in diverse cohorts are needed to determine the potential for adverse microstructural and functional change over the longer term to better guide intervention and policy, Lipton and colleagues concluded.
AuntMinnie.com · Minnies 2024 - Image of the Year
Runner up: Gallium-68 (Ga-68) prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-11 PET imaging provides clues on how men with prostate cancer respond to Pluvicto treatment. Image from Phillip Kuo, MD, PhD, of the City of Hope in Duarte, CA, and Michael Morris, MD, of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
Scientific Paper of the Year
Minnies 2024 Winner: Radiologist Workforce Attrition from 2019 to 2024: A National Medicare Analysis. Rosenkrantz, et al, Radiology, July 23, 2024. To learn more about this paper, click here.
The winner selected for Scientific Paper of the Year by the Minnies expert panel found that attrition isn’t to blame for the shortage of radiologists in the U.S.
Andrew Rosenkrantz, MD, and Ryan Cummings, MD, of NYU Langone Health in New York City, delved into Medicare billing data from 23,496 radiologists. They calculated a workforce attrition percentage by classifying providers who were consistently in practice from 2015 to 2019 and who were no longer in practice in 2024.
Among male and female radiologists, attrition rates were 13.5% and 12%, respectively. Furthermore, the researchers calculated a 6% attrition rate among those younger than 65 and 2.9% attrition in those with an estimated age of less than 45.
Moreover, attrition rates for radiologists were the second lowest among the eight specialty groups included in the analysis.
“The workforce shortage has been one of the recent top issues in radiology, with implications for burnout and care quality, but its drivers remain debated," Cummings told AuntMinnie.com. "By better understanding what is leading to the shortage, we can better develop solutions and targeted interventions for potential relief.”
As to why attrition is lower in radiology than other specialties, Rosenkrantz speculated that perhaps the rise of remote reading during the pandemic allowed a fraction of radiologists to remain in the workforce who otherwise would have retired, leading to the lower attrition in radiology than in other specialties without such an option.
“Or maybe radiology practices have been able to implement other flexible or creative workflow arrangements to keep individuals in the workforce beyond that which has been achieved by other specialties,” he told AuntMinnie.com.
Ultimately, the findings suggest that attrition – defined as switching to a different career or retiring early – is not a primary driver of the current national radiologist workforce shortage and that other potential drivers should be explored.
Rosenkrantz noted that other possible drivers are myriad, and include potentially insufficient annual influx of new radiologists, growing imaging use in certain settings (e.g., emergency), and growing demands or expectations for report turnaround times that constrain radiologists' workflow flexibility.
“And perhaps a paradoxical effect from artificial intelligence (AI) that in fact increases radiologists' time by requiring radiologists to now oversee and supervise the AI tool and evaluate its output in addition to all of the traditional tasks performed during interpretation,” he suggested.
AuntMinnie.com · Minnies 2024 - Scientific Paper of the Year
Runner up: Generative Artificial Intelligence for Chest Radiograph Interpretation in the Emergency Department. Huang, et al, JAMA Network Open, October 5, 2023. To learn more about this paper, click here.
Best New Radiology Device
Minnies 2024 Winner: Aquilion One/Insight Edition CT scanner, Canon Medical Systems
The Minnies expert panel has named Canon’s Aquilion One/Insight Edition CT scanner as this year’s Best New Radiology Device.
First unveiled at RSNA 2023, the Aquilion One/Insight Edition is Canon’s new flagship CT scanner. The scanner produces super-resolution 1024 matrix images for cardiac and body exams and features the company's AI-assisted Precise IQ Engine (PIQE) deep-learning reconstruction technology, as well as new software designed to streamline the CT workflow.
“The Aquilion One/Insight Edition stands out for Canon, offering exceptional image clarity and speed,” noted Dhruv Mehta, managing director of Canon’s CT business unit.
For instance, a completely redesigned gantry houses a new CoolNovus x-ray tube and PureInsight detector, which were designed to withstand the forces generated during the scanner’s ultrafast 0.24-second gantry rotations. The CoolNovus X-ray tube is designed for operation at 50g’s with improved heat dissipation and a longer tube life, while the PureInsight detector reduces electronic noise by up to 40%, which adds to better image quality, Canon said.
 Canon's Aquilion One/Insight Edition CT scanner. Image courtesy of Canon.
Canon's Aquilion One/Insight Edition CT scanner. Image courtesy of Canon.
The PIQE deep-learning reconstruction technology, in combination with a low kV acquisition (70 kV) and high mA (1400 mA), also makes it possible to minimize the amount of CT contrast injected in patients in vascular imaging, a particularly important feature in pediatric imaging, the company noted.
The scanner also features Canon's Instinx AI-enabled workflow software, which employs automation in steps from referral to diagnosis and is intended to make operations easier, faster, and more consistent – ultimately reducing workflows by up to 40%, regardless of various experience levels among operators, the company said. Moreover, the scanner’s 80-cm diameter and flared gantry enhance patient comfort, while two built-in cameras simplify patient positioning based on AI anatomical detection.
"With INSTINX AI-enabled workflow automation, we're streamlining the imaging process, which is particularly beneficial in high-demand healthcare settings,” Mehta added.
UC Davis Medical Center recently noted it was among the first in the U.S. to install an Aquilion One/Insight Edition, and touted its advantages in a blog post, while the first installations of the scanner in Europe came in April at the Royal Bournemouth Hospital in the U.K. and the University of Strasbourg in France.
Satrajit Misra, chief sales and marketing officer, added, “[The scanner’s] AI-driven capabilities push the boundaries of imaging quality and efficiency, translating to more streamlined patient management, particularly in challenging cases. The forthcoming enhancements we plan to showcase at RSNA 2024 will further strengthen this platform's ability to adapt to a wider range of clinical applications.”
Runner Up: NeuroLF dedicated brain PET imaging system, Positrigo
Best New Radiology Software
Minnies 2024 Winner: PowerScribe Smart Impression, Microsoft
Microsoft’s PowerScribe Smart Impression turned heads when it was introduced at the 2023 RSNA meeting in line with interest in utilizing generative AI technologies to streamline the process of creating radiology reports.
Designed to help save time and reduce workload-related stress for radiologists, Smart Impression automatically creates draft impressions and recommendations for radiology reports, according to the vendor. Trained on millions of reports, Smart Impression also offers reminders of important information to include and adapts to radiologists’ reporting style and preferences, Microsoft said.
 Smart Impression automatically creates draft impressions and recommendations for radiology reports. Image courtesy of Microsoft.
Smart Impression automatically creates draft impressions and recommendations for radiology reports. Image courtesy of Microsoft.
In addition, it utilizes structured data to automate reporting workflow and facilitate follow-up tracking. All relevant radiology findings and other available patient data are included in the reports, according to the firm.
“PowerScribe Smart Impression is the result of Microsoft’s continued advancement of generative AI to reduce administrative burden and improve clinical efficiency while also supporting better outcomes,” said Matthew Lungren, MD, chief scientific officer for Microsoft Health and Life Sciences.
AuntMinnie.com · Minnies 2024 - Best New Radiology Software
Runner-up: MIM Symphony HDR Prostate software, MIM Software
Best New Radiology Vendor
Minnies 2024 Winner: Radpair
Radpair was founded by radiologist and CEO Avez Rizvi, MD, to apply generative AI technology to develop a radiology reporting system. The zero-footprint Radpair platform includes a medical dictation system and automatically generates complete reports, including findings and impressions.
“Radiologists facing unprecedented levels of burnout, with increased demands and a workload that continues to grow,” Rizvi said. “At Radpair, we wanted to make a meaningful impact by developing solutions that ease their daily challenges, allowing them to focus more on their expertise and patient care.”
 Radpair’s automatic impressions tool is designed to deliver concise summaries of key findings, according to the vendor. Image courtesy of Radpair.
Radpair’s automatic impressions tool is designed to deliver concise summaries of key findings, according to the vendor. Image courtesy of Radpair.
Although Radpair works out of the box without any need for training, it can also be fine-tuned to suit individual users, according to the company.
Earlier in 2024, Radpair teamed up with Radiopaedia.org to launch PAIR Insights, a software feature that enables radiologists to automatically insert guidelines and classifications from Radiopaedia directly into their reports.
Recently, the company launched version 2.0 of its Radpair platform. Radpair 2.0 features a new user interface and also Groq LPU AI inference technology. The new release also brings advanced report preprocessing, “intelligent” AI editing, and a proprietary report verification system, according to the vendor.
“Radiology is at a crossroads - our technology is designed to meet this moment by offering radiologists tools that enhance their efficiency and ease daily demands,” Rizvi said. “We’re proud to help these invaluable professionals find joy in their work again.”
AuntMinnie.com · Minnies 2024 - Best New Radiology Vendor
Runner-Up: Springbok Analytics
Best Educational Mobile App
2024 Minnies Winner: MRI Made Easy... well almost, BestApps (iOS)
MRI Made Easy is now the second Minnies winner among the popular family of doRadiology educational mobile apps. It joins Radiology Assistant 2.0, a two-time champion and also this year’s runner-up.
Available for free, MRI Made Easy is an animated, dynamically indexed, and interactive educational tool designed to make the complex field of MRI physics accessible and engaging, according to Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD, of the University Medical Center Utrecht.
“We believe that to really master reading MRI, you have to know MRI physics,” Veldhuis told AuntMinnie.com.
 MRI Made Easy is an animated, interactive app designed to help educate users about MRI physics. Image courtesy of Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD.
MRI Made Easy is an animated, interactive app designed to help educate users about MRI physics. Image courtesy of Wouter Veldhuis, MD, PhD.
The app was originally inspired by the classic book, MRI Made Easy, by Prof. Hans Schild of Radiological University Hospital Bonn in Germany, Veldhuis said. Its primary audience is radiology residents, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals interested in improving their understanding of MRI physics.
“It is particularly suited for those who prefer a modern, interactive learning format over a traditional textbook,” Veldhuis said.
With MRI Made Easy, users can either read the contents from cover to cover, or drill down to specific concepts from the dynamically updated index, he said.
“So it's useful both as a teaching resource and as a reference for looking up physics topics,” he said. “The app expanded on the original static drawings and recreated many in animated form, which really helps the understanding of complex concepts.”
Furthermore, the app’s Quiz Mode enables users to test their understanding of MRI physics, with answers that directly reference the full text, he said.
The app has been downloaded hundreds of times each month for the past eight and a half years and now has more than 40,000 users in 135 countries, according to Veldhuis.
Runner-Up: Radiology Assistant 2.0, BestApps (iOS)