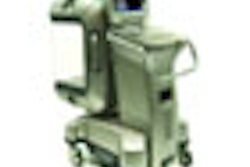
(Booth 1729) GE Healthcare of Chalfont St. Giles, U.K., will showcase its latest multidetector CT scanner, the LightSpeed VCT XT, as well as radiation dose reduction technology and new advancements designed to dramatically improve image quality.
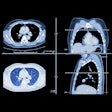
On the dose reduction side, SnapShot Pulse was first introduced at the 2006 RSNA show, and is designed to reduce patient radiation exposure by up to 70% as images of the heart and coronary arteries are captured in as few as five heartbeats.
While a typical helical CT scan of the heart would produce between 6 mSv and 20 mSv of radiation, SnapShot Pulse can reduce the dose to between 1 mSv and 6 mSv, according to a GE spokesperson.
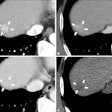
In addition to SnapShot Pulse, GE will highlight its VolumeShuttle technology, designed to address the need for wide coverage in both angiography and perfusion studies and to enable whole-organ visualization. VolumeShuttle is capable of doubling the width of anatomic coverage without an increased radiation dose, and within a single contrast injection.
Finally, look for GE to discuss a package of technologies it's calling the HD platform, which is designed to produce much higher image quality on the company's 64-slice scanners. HD technologies include adding the ability to tune the size of the x-ray beam's focal spot to match the type of study being conducted, with smaller focal spots producing better resolution. The HD platform will also employ a new detector to resolve smaller regions of interest, and a new reconstruction engine with iterative reconstruction rather than 3D filtered back-projection reconstruction to process larger amounts of data.