Chinese researchers performing coronary CT angiography (CCTA) on a wide-area CT scanner with 640-slice reconstruction found they could substantially reduce the use of contrast media -- at least in nonobese patients with well-controlled heart rates.
The researchers scanned more than 100 patients using contrast volumes of 0.8, 0.7, or 0.6 mL/kg, measuring CT attenuation in the ascending and descending aorta, left and right coronary arteries, and coronary sinus. CT values in the ascending and descending aorta and coronary arteries exceeded 300 HU in all three contrast groups.
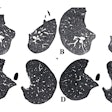
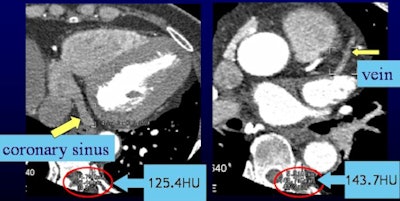
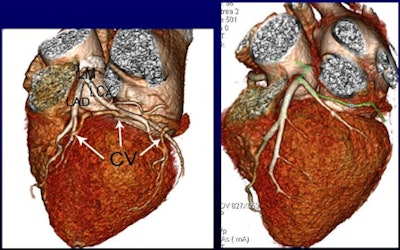 More contrast volume in the whole-heart CT image from group A (0.8 mL), left, resulted in better enhancement of the coronary sinus and veins compared to group C (0.6 mL) at right. The group C image is still diagnostic, however. All images courtesy of Ding Zhong-Xiang.
More contrast volume in the whole-heart CT image from group A (0.8 mL), left, resulted in better enhancement of the coronary sinus and veins compared to group C (0.6 mL) at right. The group C image is still diagnostic, however. All images courtesy of Ding Zhong-Xiang."We found that reduced contrast methods were clinically feasible because of the advantage of 640-slice volume CT and small [body mass index (BMI)] Asian patients," lead researcher Ding Zhong-Xiang told AuntMinnie.com. "We use this method as our routine protocol now." The study was originally presented at the 2013 European Congress of Radiology (ECR).
Coronary CT angiography is a useful test for detecting coronary artery disease, but the high contrast doses required are worrisome due to the potential risk of contrast-induced nephropathy in vulnerable patients, said Zhong-Xiang, a radiologist at Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital.
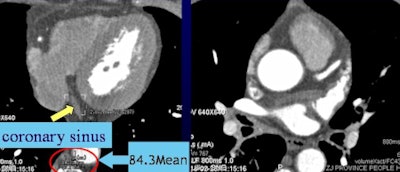
 Above, more volume of contrast agent in group A resulted in more enhancement of the coronary sinus and veins. Conversely, below, less volume of contrast agent in group C resulted in less enhancement.
Above, more volume of contrast agent in group A resulted in more enhancement of the coronary sinus and veins. Conversely, below, less volume of contrast agent in group C resulted in less enhancement.
A 640-slice dynamic volume CT scanner (Aquilion One, Toshiba Medical Systems) utilizes 320 detector rows with 640-slice reconstruction, and the scanner's 16-cm anatomic coverage means the entire heart can be scanned in a single beat (one 0.35-sec rotation). This offers the potential for more efficient utilization of contrast, with substantial reduction in the volumes needed to create diagnostic images, Zhong-Xiang said. With this in mind, the study aimed to optimize the contrast injection protocols for coronary CTA.
Zhong-Xiang and his colleague Zhen Wang examined a total of 105 patients with suspected coronary artery disease and low heart rates of 65 beats per minute or less. The patients were randomly divided into three groups of 35 subjects each; they were then injected with one of three amounts of iodinated contrast at 5 mL/sec, followed by a 30-mL saline flush at the same rate.
| Contrast protocols | |||
| Group | Mean injection volume (at 5 mL/sec) |
Mean contrast volume | Mean scan delay after injection |
| A | 0.8 mL | 54.1 mL | 23.7 sec |
| B | 0.7 mL | 47.9 mL | 23.4 sec |
| C | 0.6 mL | 41.1 mL | 22.2 sec |
The study team measured attenuation at regions of interest in the ascending and descending aorta, left and right coronary arteries, and coronary sinus.
CT values in the coronary sinus were 112.7, 93.7, and 81.2 HU for Groups A, B, and C, respectively (p < 0.001). CT values within the ascending and descending aorta and the coronary arteries were higher than 300 HU in all three contrast groups.
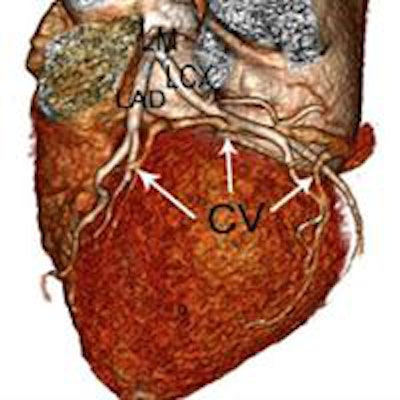
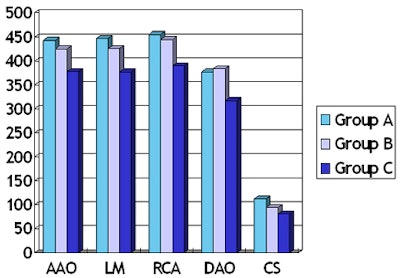 CT values within the ascending and descending aorta and the left main and right coronary artery orifices were higher than 300 HU. AAO = ascending aorta; LM = left main coronary artery; RCA = right coronary artery; DAO = descending aorta; CS = coronary sinus.
CT values within the ascending and descending aorta and the left main and right coronary artery orifices were higher than 300 HU. AAO = ascending aorta; LM = left main coronary artery; RCA = right coronary artery; DAO = descending aorta; CS = coronary sinus.CCTA protocols limited to 0.6 mL/kg of contrast, with homogeneous enhancement in the coronary arteries, can be achieved using 640-slice volume CT, Zhong-Xiang concluded.