Wednesday, December 3 | 3:00 p.m.-3:10 p.m.| SSM25-01 | Room E450B
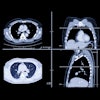
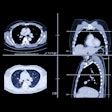
Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the gold standard for evaluating arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), but 4D CT angiography (CTA) outperforms it by visualizing the nidus.Such visualization is crucial because it reduces radiation dose and results in better treatment planning, according to Dutch researchers.
The study team from Radboud University in Nijmegen performed DSA in 18 patients, along with CTA on a 320-detector-row scanner (Aquilion One, Toshiba Medical Systems). Alternate readings were performed to maximize the diagnostic information from each scan, and radiation dose was calculated.
Diagnostic information and treatment planning with 4D CTA were better than with DSA in 11 (61%) of the 18 patients, equivalent in 22%, and inferior in 17%, the authors reported. Radiation dose from CT was a little over half that of DSA.
"Localization of the nidus is of paramount importance in the treatment of patients with arteriovenous malformations," wrote co-author Dr. Ritse Mann, PhD, in an email to AuntMinnie.com. "Our study shows that 4D CTA may improve nidus localization and thus therapy planning, while reducing the radiation exposure."