Dear CT Insider,
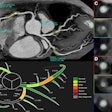
In recent years, a bevy of studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of using CT scans to calculate fractional flow reserve (FFR) noninvasively. One group took this concept to the next level in research presented at RSNA 2017.
The researchers from the Medical University of South Carolina used a machine-learning algorithm to analyze FFR-CT data. Their goal was not only to identify which patients with coronary artery disease required revascularization, but also to determine the best revascularization procedure for them. Get the details on how machine learning of FFR-CT could help guide therapeutic management in our Insider Exclusive.
The recent RSNA 2017 meeting in Chicago was also teeming with other CT news and research:
- A group from the Einstein Healthcare Network demonstrated a method for reducing variation in CT radiation dose throughout its entire Pennsylvania network.
- Researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School investigated the differences in identifying stenosis when radiologists viewed coronary CT angiography (CCTA) scans at core labs versus local healthcare institutions.
- A team from Rome used iterative reconstruction to sharply reduce the radiation dose necessary to collect calcium scores from CCTA scans.
- Dutch researchers developed a deep-learning algorithm to quantify coronary artery calcium scores from CT lung cancer screening exams.
- Dozens of radiologists from various Italian universities and hospitals united in a collaborative effort to identify cadavers of a mass disaster using mobile CT.
- Researchers from Thomas Jefferson University reported shifting trends in the usage rate of CCTA. Their study answers the question: Do radiologists or cardiologists now predominate in CCTA use?
This list represents just a selection of new research covered in our CT Community. Head over to AuntMinnie.com for more updates in the field all throughout the holiday season.