Monday, November 26 | 11:20 a.m.-11:30 a.m. | SSC01-06 | Room S504CD
A group from Italy found that stress coronary CT perfusion in addition to coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can enhance the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients at intermediate to high risk for the disease.Previous research has shown that CT perfusion (CTP) could potentially add value to the assessment of patients at high risk of CAD, according to the researchers from Centro Cardiologico Monzino in Milan.
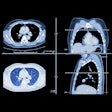
In this prospective study, Dr. Giuseppe Muscogiuri and colleagues searched for the presence of hemodynamically relevant stenosis (≥ 50% stenosis) and heart wall thickening in 48 patients who underwent CCTA and CT perfusion exams at the hospital. The average radiation exposure from CT perfusion was approximately 5 mSv.
The investigators identified obstructive CAD in nearly 40% of all vessels in almost 75% of the patients using invasive coronary angiography.
Compared with invasive coronary angiography, CCTA alone demonstrated high sensitivity but relatively low specificity and accuracy in ruling out CAD. In contrast, CCTA with CT perfusion produced comparable sensitivity but statistically significant increases in specificity and diagnostic accuracy (p < 0.001).
These findings suggest that CT perfusion can add considerable value to the diagnosis of obstructive CAD in patients suspected of being at intermediate to high risk of CAD, Muscogiuri told AuntMinnie.com.
"Considering that the mean radiation exposure of the dynamic CTP protocol was 5.3 mSv, the addition of dynamic stress CTP to coronary artery imaging by CCTA provides additional diagnostic accuracy with acceptable radiation exposure," he said.