Monday, December 2 | 11:40 a.m.-11:50 a.m. | SSC01-08 | Room S402AB
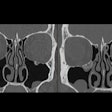
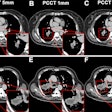
Fractional flow reserve CT (FFR-CT) values measured in the distal segment of the coronary arteries were markedly lower than those measured in the proximal and mid segments of the same arteries in a study by researchers from South Carolina.Onsite FFR-CT analysis using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms could produce different values depending on the region of the coronary artery examined even in patients without coronary artery disease, according to presenter Marly van Assen, a doctoral candidate at the Medical University of South Carolina.
The researchers performed FFR-CT analysis on the coronary CT angiography (CCTA) scans of approximately 100 patients who had no levels of coronary artery calcium and no signs of any cardiac abnormality. Roughly 28% of the cohort's coronary arteries were associated with a positive FFR-CT score (less than 0.75) despite not having stenosis.
Further analysis revealed that this high false-positive rate was a result of discrepancies in FFR-CT values based on the region of the coronary arteries examined. To be specific, the FFR-CT values obtained from the distal segment of the arteries had a lower specificity and positive predictive value than those from more proximal segments.
"FFR-CT values can become abnormal at a distal location without indicating flow-limiting stenosis and are strongly influenced by a decrease in Hounsfield unit values," van Assen told AuntMinnie.com. "CT-FFR values measured distal should always be interpreted in combination with the CCTA images."