Researchers from China have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm that accurately detects COVID-19 and differentiates it from community-acquired pneumonia and other lung diseases. They shared their results in an article published online March 19 in Radiology.
In a multicenter effort, co-lead authors Lin Li of Wuhan Huangpi People's Hospital and Lixin Qin of Wuhan Pulmonary Hospital and colleagues developed COVNet, a deep-learning model that could find COVID-19 on chest CT exams with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.96. What's more, it could also identify community-acquired pneumonia with an AUC of 0.95 and was highly accurate for other nonpneumonia conditions.
"These results demonstrate that a machine-learning approach using a convolutional networks model has the ability to distinguish COVID-19 from community-acquired pneumonia," the authors wrote.
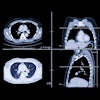
To develop a deep-learning model that could handle the difficult task of differentiating between COVID-19 and other types of pneumonia on CT, the researchers first retrospectively acquired a dataset of 3D volumetric chest CT exams for 1,296 COVID-19, 1,735 community-acquired pneumonia, and 1,325 nonpneumonia cases from six centers in China. The nonpneumonia group included patients with no lung disease, lung nodules, chronic inflammation, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or other diseases such as pneumothorax or tracheal diverticulum.
The CT exams were acquired using equipment from different manufacturers but with standard imaging protocols. All COVID-19 cases were confirmed as positive via nucleic acid testing with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing and were acquired between December 31, 2019, and February 17, 2020, according to the researchers.
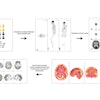
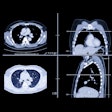
Of the exams, 90% were randomly placed into the training dataset. The remaining 10% were used for validation and testing of COVNet, a 3D deep-learning framework that's capable of extracting both 2D and 3D image features. After analyzing the image, COVNet provides a probability score for each of the three classes of conditions: COVID-19, community-acquired pneumonia, and nonpneumonia.
In addition, the model provides a heat map to highlight the important regions of the image that led to its decision. It took an average of 4.51 seconds for the algorithm to process each CT exam in the testing dataset.
| Performance of deep-learning model for COVID-19 | |||
| Nonpneumonia | Community-acquired pneumonia | COVID-19 | |
| Sensitivity | 94% | 87% | 90% |
| Specificity | 96% | 92% | 96% |
| AUC | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
The researchers emphasized that no single method will be able to differentiate all lung diseases based only on their appearance on chest CT.
"There is overlap in the chest CT imaging findings of all viral pneumonias with other chest diseases that encourages a multidisciplinary approach to the final diagnosis used for patient treatment," they wrote.
The authors also noted that the model focuses on identifying the presence of COVID-19 but does not categorize the disease into different severities.
"As a next step, it would be important to not only predict the presence of COVID-19 but also the severity degree to further help monitor and treat patients," they wrote.