CT shows that COVID-19 patients are at increased risk of acute kidney injury, and thus at higher risk of tragic outcomes such as multiple organ failure and death, according to a study published June 2 in Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.
The study findings should help clinicians better understand the effects of severe COVID-19, wrote a team led by Dr. Natalia Chebotareva of Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University in Russia.
"Acute kidney injury is a serious complication of COVID-19, which also determines the prognosis of the disease ... [and] studies have demonstrated that the development of acute kidney injury is associated with high risk of death in patients with COVID-19," the group wrote.
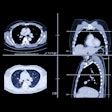
COVID-19 most often initially presents as a respiratory disease. But as the pandemic has continued, clinicians have learned that it also affects the kidneys, the heart, the gastrointestinal tract, and the nervous system. Studies have shown that many of COVID-19 patients develop acute kidney injury, with frequency rates ranging from 0.5% to 28%, according to the authors.
Chebotareva and colleagues sought to further investigate the connection between incidence of acute kidney injury and death in COVID-19 patients through a study that included 1,280 patients with COVID-19 confirmed by a reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction test. The researchers tracked patients' demographic data, associated comorbidities (such as diabetes and hypertension), CT exam and lab test results, and treatments used to deal with COVID-19 in order to assess the incidence of acute kidney failure. Treatments consisted of retroviral therapy, the use of glucocorticoids, and breathing/kidney support.
Of the study cohort, 648 (50.6%) patients were diagnosed with proteinuria, a sign of kidney damage. Acute kidney injury was diagnosed in 371 patients, or 29%; of these, 10 (2.7%) required dialysis.
The researchers found the following risk factors for acute kidney injury among COVID-19 patients:
- Older than 65
- High levels of C-reactive protein and ferritin
- More severe lung involvement
- Increased blood coagulation time (as measured by activated partial thromboplastin testing)
Overall, 162 (12.7%) of the 1,280 COVID-19 patients died. Of 371 COVID-19 patients with acute kidney injury, 111 died (29.9%). Patients with acute kidney injury had almost four times higher risk of death than those without the condition (hazard ratio, 3.96).
Acute kidney injury in COVID-19 patients all too often translates into increased risk of mortality, according to the group.
"Two factors that influence acute kidney injury development [in COVID-19 patients] are old age and hyperactivation of the inflammatory response," the team concluded. "In addition, DIC [disseminated intravascular coagulation] and the severity of lung involvement were associated with severe acute kidney injury development. An increased risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19 was connected to the same factors and the presence of arterial hypertension."