Monday, November 29 | 3:00 p.m.-3:10 p.m. | SSE06-01 | Room S404CD
Researchers from the University of Chicago were able to improve the sensitivity of computer-aided detection (CAD) in detecting lung nodules -- presenter Sheng Chen will share their results in this Monday afternoon session.One of the major challenges in the current use of CAD is detecting nodules that overlap with ribs. In addition, ribs are a frequent cause of false-positive marks, according to Chen.
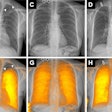
In the hope of rectifying this problem, the researchers aimed to develop a CAD scheme that incorporates virtual dual-energy (VDE) technology, which offer suppression of the ribs on chest x-rays via a massive-training artificial neural network (MTANN).
In testing on a database of 126 nodules on 126 chest x-rays, the use of VDE images increased the CAD software's sensitivity from 63.5% to 73%, with the same false-positive rate.
"[CAD] with a high sensitivity for subtle nodules and a low [false-positive] rate would be useful for radiologists in detecting such lung nodules in [chest x-rays]," Chen told AuntMinnie.com. "By using VDE images, the sensitivity and specificity of our [CAD] scheme for nodule detection in [chest x-rays] were improved substantially."