CHICAGO - At this week's RSNA 2010 meeting in Chicago, Toshiba America Medical Systems of Tustin, CA, is highlighting its ongoing work to reduce CT radiation dose. The firm is also touting upgrades within its ultrasound, MRI, and x-ray product lines.
CT
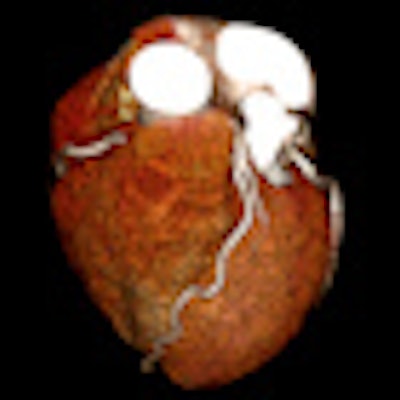
Toshiba's CT dose reduction efforts revolve around two technologies, adaptive iterative dose reduction (AIDR) and Target CTA. AIDR involves multiple iterative reconstructions to reduce radiation dose and improve image quality, while Target CTA makes use of the Aquilion One scanner's ability to scan the heart in one rotation to improve organ targeting and minimize padding of the scan range. The technique is most useful during gated cardiac studies.
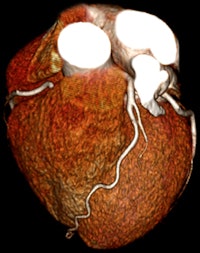 |
| Low-dose prospective cardiac CTA image acquired in one gantry rotation on Aquilion One. |
The protocol can perform a pulmonary embolism scan in 2.3 seconds; whole-body scans can be performed in 3.1 seconds with a CT dose index volume (CTDIvol) of 7.5 mGy, compared to American College of Radiology (ACR) reference values of 25 mGy or less for abdominal scanning. The scanning mode is particularly well-suited for patients who have difficulty staying still during studies, such as trauma patients.
Toshiba is also highlighting clinical research under way on the effects of Aquilion One on the economics of treating stroke patients. Researchers at Millard Fillmore Gates Circle Hospital in Buffalo, NY, are using CT rather than MRI for stroke assessment, and they're finding that using the 320-detector-row Aquilion One system produces savings of $762,000 a year by changing patient workup and reducing length of stay.
Ultrasound
In ultrasound, Toshiba is highlighting a series of upgrades for its scanners, as well as a women's imaging configuration for its Aplio XG system.
The women's imaging package includes several Toshiba applications, including elastography, MicroPure for detecting breast calcifications, Dynamic Micro Slice with an ultrawide-band 18-MHz transducer, and improvements in 4D scanning that allow physicians to view all imaging planes during biopsy for more precise needle guidance, for example.
For its cart-based ultrasound scanners (Aplio XG, Aplio MX, and Xario XG), Toshiba is highlighting upgrades that include new transducers, 4D imaging improvements, and workflow protocol enhancements. Workflow improvements include protocols that can be easily set up, such as giving sonographers the ability to add custom annotations and manually shuffle images. Users also have one-touch access to Toshiba's iAssist scanning protocols.
 |
| Toshiba's RadRex-i x-ray system. |
For the compact Viamo scanner, Toshiba is adding high-end features found on its cart-based line, such as ApliPure and TissuePure Imaging modes and DICOM Structured Reporting. The scanner also now supports imaging up to a depth of 40 cm, which should make the system more suitable for larger patients.
X-ray and angiography
In x-ray, Toshiba is demonstrating a new digital detector panel for the company's Kalare combined radiography and fluoroscopy unit. The panel, a 14 x 17-inch CXDI-55G detector from Canon U.S.A. of Lake Success, NY, is thinner and lighter than the previous panel used on Kalare, and it's now positioned in a rotating bucky tray so technologists no longer need to lift the panel to reposition it.
Toshiba is also highlighting dose reduction technologies available on Kalare, such as a last image hold feature, virtual collimation, and grid-controlled pulse fluoroscopy.
For the RadRex-i system, Toshiba has made upgrades to the unit to make it compatible with the Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) standard, such as supporting DICOM Dose Structured Reporting. Other changes include a more compact patient stand for scoliosis imaging and a lateral cassette holder that pivots out and drops down for more flexible cross-table imaging. The system's RexView technologist control panel has also been enhanced.
On in the Infinix-i angiography system, new developments include Volume Navigation, a new 3D roadmapping technique that puts 3D images on 2D fluoroscopy studies, and links system movements to the roadmap. Toshiba has also made changes to the system's source-to-image distance (SID) and field-of-view.
 |
| Toshiba's Infinix-i angiography system. |
For the Infinix VF-i biplane system, Toshiba is highlighting midsized 12 x 12-inch digital detectors; the wider field-of-view makes the system better suited for cerebral studies, full-body imaging, and implant guidance.
MRI
In MRI, Toshiba expects to receive 510(k) clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) later this year for Vantage Titan, the company's entry into the 3-tesla MRI segment. Toshiba is discussing a new M-Power user interface, which enables users to employ fewer mouse clicks when preparing sequences, such as its m-Vox isotropic brain imaging protocol.
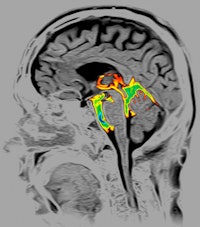 |
| Image of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain acquired with Toshiba's Time-SLIP MRI protocol. |
Toshiba has also upgraded its 1.5-tesla Vantage Titan scanner with a new configuration known as Vantage Titan HSR. The enhancements include high slew rate gradients (gradient strength of 30 mT/m and slew rate of 203 mT/m/msec) and the M-Power user interface found on the 3-tesla model. Vantage Titan HSR is pending 510(k) clearance.
By Brian Casey
AuntMinnie.com staff writer
December 1, 2010
Related Reading
Toshiba touts noncontrast renal MRA trial, November 30, 2010
Toshiba adds 3D roadmap software, November 25, 2010
Toshiba to debut new M-Power interface, November 23, 2010
Toshiba rolls out new RadRex-i DR system, November 16, 2010
Toshiba debuts 32-element MRI coils, November 9, 2010
Copyright © 2010 AuntMinnie.com