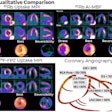
| FIGURE 1.1.2 Sessile advanced adenomas. 3D endoluminal CTC image (A) shows a 1.5-cm polyp on a colonic fold. Note the adjacent diverticula. 3D colonic map (B) shows the location of the large polyp in the descending colon (arrow), in addition to multiple left-sided diverticula. Digital photograph from same-day colonoscopy (C) shows the same polyp on a fold, which proved to be a tubulovillous adenoma. Prone 3D endoluminal (D) and supine transverse 2D (E) images from a second patient show a 2-cm lobulated sessile polyp in the rectum, which is submerged on the supine view but visible due to contrast tagging of the fluid. Corresponding colonoscopy image (F) shows the same lesion, which proved to be a tubulovillous adenoma. 3D endoluminal CTC (G), 2D transverse CTC (H), and corresponding colonoscopy (I) images from a third patient show a large polypoid rectal mass, which is separated from the rectal catheter at CTC by a rectal fold. This 3-cm sessile mass proved to be a tubulovillous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia. |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 1.1.2 Sessile advanced adenomas
Latest in Home
AI boosts cardiac PET imaging
September 8, 2025
Neuroradiology still lacks gender, racial/ethnic diversity
September 8, 2025
PET use increasing in diagnosing cardiac device infections
September 5, 2025