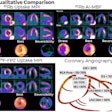
| FIGURE 1.1.7 Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Contrast-enhanced CT images (A and B) show multiple polypoid soft tissue lesions within the contrast-filled colon, including a dominant polypoid mass (asterisk) in the ascending colon. Images from subsequent colonoscopy (C and D) again demonstrate the multiple adenomatous polyps and the larger mass, which proved to be a tubulovillous adenoma with multiple foci of adenocarcinoma. Note the "cerebriform" appearance to the overlying mucosa often seen with adenomatous neoplasia. Double-contrast BE images (E and F) from two different patients with FAP show innumerable sessile filling defects representing adenomas. (A to D from Pickhardt PJ: Differential diagnosis of polypoid lesions seen at CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy). Radiographics 2004; 24:1535-1559.) |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 1.1.7 Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Latest in Home
AI boosts cardiac PET imaging
September 8, 2025
Bayer pivots away from AI platform business
September 8, 2025
PET use increasing in diagnosing cardiac device infections
September 5, 2025