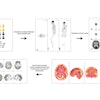
| FIGURE 2.1.3 Severe ulcerative colitis. Transverse (A) and coronal (B) contrast-enhanced CT images show multiple enhancing polypoid lesions in the sigmoid colon, representing inflammatory pseudopolyps. Note the changes of long-standing UC, consisting of ahaustral foreshortening of the entire colon and mild uniform wall thickening. At colonoscopy (C), the pseudopolyps are evident and the mucosa appears friable and ulcerated. Contrast-enhanced CT images (D and E) from a second patient show marked low-attenuation wall thickening of the entire colon, with mucosal and serosal enhancement. Pancolitis in this case is more prominent than usual for UC, and the CT appearance may suggest Clostridium difficile or granulomatous colitis. Colonoscopy image (F) from a third patient shows extensive pseudopolyp formation with advanced hemorrhagic inflammation and mucosal friability. |
Atlas of Gastrointestinal Imaging Figure 2.1.3 Severe ulcerative colitis
Latest in Home
Bone-RADS improves accuracy for junior, attending physicans
October 17, 2025
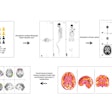
PET/CT reveals ‘chemo brain’ regions in leukemia patients
October 16, 2025