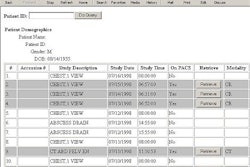
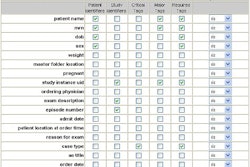
| Summary of Wireless Security Standards |
|
 |
|
| A. Bluetooth Protocol | |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
| B. Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) | |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
| C. Wireless Local Area Networks (WLANs), IEEE 802.11 | |
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
Summary of Wireless Security Standards
Jun 8, 2003
Latest in PACS/VNA
GE HealthCare launches Genesis portfolio on AWS Marketplace
September 23, 2025
Sectra reports sales, profit increases for Q1
September 4, 2025
Radpair partners with AdvaHealth Solutions on AI platform
August 21, 2025
MedDream launches latest version of DICOM viewer
August 13, 2025