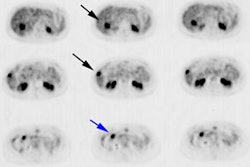
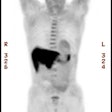
PET Oncologic Imaging
Latest in PET
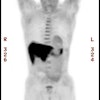
PET > PET tumor imaging > Neuroendocrine tumors
April 14, 2021
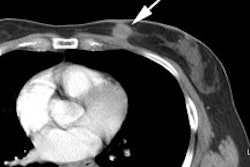
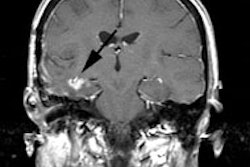
PET > PET tumor imaging > Head and Neck Tumors
March 12, 2018
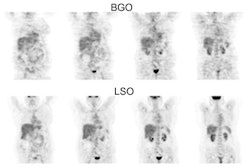
PET > General > Images
January 23, 2018
PET > PET tumor imaging > Prostate cancer
January 20, 2016