Integrating AI-powered image reconstruction into MR imaging significantly improves image quality and diagnostic confidence compared with conventional MRI, according to findings delivered at the recent RSNA meeting.
It also improves patients' experience of the exam, said presenter Patricia M. Carrascosa, MD, PhD, of Diagnóstico Maipú por Imágenes in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
"[We found that] the integration of AI-powered image reconstruction in MRI significantly enhanced image quality and diagnostic confidence, demonstrating high sensitivity and specificity," Carrascosa explained. "Additionally, AI-driven acceleration led to a substantial reduction in scan duration, improving patient comfort and overall experience."
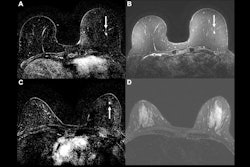
Carrascosa and colleagues conducted a study that included 331 patients who underwent MR imaging of the knee, hip, and shoulder. Each exam was performed using AI-based image reconstruction technology (AIR Recon DL, GE HealthCare) as well as an additional sequence without AI assistance.
Radiologist readers assessed image quality using a three-point scale (1 = regular, 2 = good, 3 = excellent). The researchers evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of the exams with AI support based on pathological findings. The AI-assisted MRI exams' scan times were reduced by 50% compared with the conventional MRI scans, Carrascosa noted.
"Low scan times benefit very symptomatic, pediatric, or claustrophobic patients," she said.
Patients completed a post-exam survey that assessed their perception of exam length, using another three-point scale, with 1 equal to "very short/short"; 2 equal to "usual/indistinct"; and 3 equal to "long/very long."
The team reported the following:
- AI-assisted MRI exams achieved a mean image quality rating of 2.6, compared with 2.2 in the conventional group.
- AI-assisted MRI exams showed a sensitivity of 99%, specificity of 86%, positive predictive value (PPV) of 95%, and negative predictive value (NPV) of 94%.
- 85% of patients rated AI-assisted MRI exams as short or very short. In contrast, 40% of patients ranked conventional MRI exam duration as "normal" and 45% ranked it as "long/very long."
"[Our] findings highlight the clinical value of AI in MRI, optimizing workflow efficiency while maintaining high diagnostic performance," Carrascosa concluded.