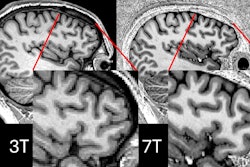
7-tesla MRI is redefining neuroradiology by offering improved sensitivity and resolution for detecting small lesions, vascular abnormalities, and microstructural changes, according to a clinical review published December 18 in RadioGraphics.
The future looks bright for the technology, wrote a team led by Seyed Seyedsaadat, MD, of Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
"As ongoing technical challenges are resolved, it is anticipated that continuous advancements will promote [7-tesla MRI's] routine clinical integration, establish novel imaging biomarkers, and broaden its clinical applications in management of neurologic disorders," the group explained.
The advent of 7-tesla MRI represents "a remarkable advancement in the field of neuroimaging," the researchers wrote, noting an increase in its clinical use after regulatory approval for brain and knee imaging.
The researchers listed 7-tesla MRI's particular benefits for a range of conditions, including epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, pituitary imaging, unruptured intracranial aneurysms, steno-occlusive conditions, primary brain tumors, cerebral cavernous malformations, cerebral amyloid angiopathy, deep-brain stimulation targeting, Alzheimer's disease, and motor neuron diseases.
They described its advantages:
- Superior signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio improve the detection and characterization of focal cortical dysplasia and other epileptic foci, which are frequently not identified on conventional MRI.
- Enhanced spatial resolution, prolonged T1 relaxation, and increased susceptibility contrast at 7-tesla improve detection of cortical demyelinating lesions, which are often missed at lower field strengths. "Overall, 7-tesla MRI allows detection of approximately 73% more cortical lesions than does 3-tesla MRI," the investigators wrote.
- Previous research has suggested that that 60% of patients who undergo 7-tesla MRI show a greater number of microbleeds than found on 3-tesla MRI, with 7-tesla MRI identifying 122% more. "What is perhaps even more striking is that 80.6% of healthy participants who had no hemorrhage at 3-tesla MRI had one or more microbleeds detected at 7-tesla MRI," Seyedsaadat and colleagues noted.
- The combination of increased signal-to-noise ratio, spatial resolution, and T2* effects "leads to improvements in the diagnostic utility of the swallow tail sign" at 7-tesla MRI versus 3-tesla MRI, with 96% and 86% accuracy, respectively, they wrote.
 Incidentally discovered aneurysm at CT angiography performed for stroke evaluation in a 61-year-old man. (A) Coronal 10-mm maximum intensity projection (MIP) 3-tesla MRA image shows a small outpouching (arrow) from the basilar summit, which was interpreted as an aneurysm. (B) Coronal image from 7-tesla MRA shows a thalamoperforator artery (arrowhead) arising from the apex of the outpouching (arrow), consistent with an infundibulum.RSNA
Incidentally discovered aneurysm at CT angiography performed for stroke evaluation in a 61-year-old man. (A) Coronal 10-mm maximum intensity projection (MIP) 3-tesla MRA image shows a small outpouching (arrow) from the basilar summit, which was interpreted as an aneurysm. (B) Coronal image from 7-tesla MRA shows a thalamoperforator artery (arrowhead) arising from the apex of the outpouching (arrow), consistent with an infundibulum.RSNA
The authors concluded that 7-tesla MRI has begun to serve as a "crucial diagnostic tool, particularly in cases where conventional MRI yields inconclusive results, thereby contributing to early diagnosis, surgical planning, and disease monitoring."
The complete review can be accessed here.