Thanks in large part to funding from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH), Johns Hopkins University spin-off Clear Guide Medical has developed technology for facilitating ultrasound-guided procedures. The funding was provided by NIH's National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB).
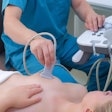
Consisting of a small touchscreen module, a handheld probe, and a cable, Clear Guide's technology allows physicians to plan needle entry and a precise line to the target before beginning the procedure, according to NIBIB. After placing the tip of the needle on the skin above the organ to be biopsied, the Clear Guide software integrates the needle angle and the ultrasound image to show the physician the path the needle would take if inserted at that precise spot.
Physicians can adjust the spot and angle of needle insertion until Clear Guide indicates it is in the position needed to hit the target, according to NIBIB. They can then insert the needle and follow the trajectory shown on the screen directly to the target.
No new hardware needs to be installed, and the system's low cost and portable design will allow primary care personnel to conduct needle biopsies in a primary care office or mobile health unit, NIBIB said. The system is designed for use in ultrasound-guided procedures such as needle biopsies, central line insertion, and local anesthesia.
A spin-off from the Johns Hopkins computer science and radiology departments, Clear Guide was founded in 2010 and received several Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) grants from NIBIB and the National Cancer Institute to help with the commercialization process and applying for U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance.
In addition to its flagship Clear Guide One software, the company has developed Clear Guide Edu, a training system for physicians to practice general needle-guided interventions in nonclinical settings.
Clear Guide's current focus is getting the product manufactured, putting quality control systems in place, and setting up international distribution agreements. Plans for a next-generation device include adding capabilities that will enable ultrasound to handle some of the procedures currently performed with CT guidance, NIBIB said.