Graphics processing unit (GPU) technology developer Nvidia has launched an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered supercomputer in the U.K. that enables researchers in digital biology and genomics.
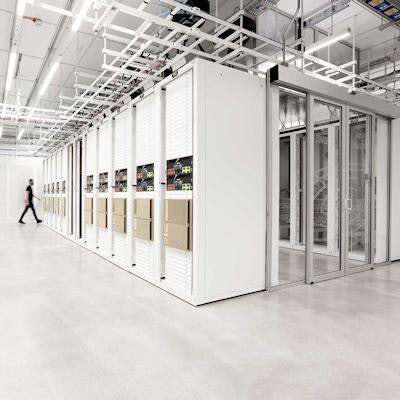
Called Cambridge-1, the supercomputer is designed to bolster research in the life sciences industry and represents a $100 million investment by Nvidia. The computer is part of an Nvidia DGX SuperPOD cluster, and it also supports the company's Clara framework and AI to enable large-scale research.
The first research projects with Cambridge-1 are being conducted by AstraZeneca, GSK, Guy's and St. Thomas' National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust, King's College London, and Oxford Nanopore Technologies. They include research into developing a better understanding of brain diseases, using AI to develop new drugs, and improving the accuracy of locating disease-causing variations in human genomes.
 Nvidia's Cambridge-1 supercomputer. Image courtesy of Nvidia.
Nvidia's Cambridge-1 supercomputer. Image courtesy of Nvidia.Over the next 10 years, the Cambridge-1 supercomputer has the potential to create an estimated value of 600 million pounds (about $828 million), according to an estimate by economics consulting firm Frontier Economics.
Cambridge-1 is being used on the following projects:
- AstraZeneca is hoping to ramp up drug discovery by creating a transformer-based generative AI model called MegaMolBART for chemical structures. A separate collaboration between Nvidia and AstraZeneca focuses on digital pathology.
- GSK is focusing on genetically validated targets for drug candidates. These are twice as likely to become commercially available medicines and are now more than 70% of the company's research pipeline.
- Generating synthetic brain images from MRI scans is the focus of research being conducted by King's College London and Guy's and St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust. Cambridge-1 will be used to teach AI models to generate synthetic images by analyzing tens of thousands of actual MRI brain scans, with the goal being to gain a better understanding of brain diseases like dementia, stroke, brain cancer, and multiple sclerosis.
- Oxford Nanopore is using Cambridge-1 to further its research into genomic sequencing platforms and build AI algorithms to improve genomic analysis. AI algorithms will be developed far more quickly, and this will improve genomic accuracy, according to Nvidia.