J Nucl Med 2001 Feb;42(2):248-56
Quantitative PET studies in pretreated melanoma patients: a comparison of
6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa with 18F-FDG and (15)O-water using compartment and
noncompartment analysis.
Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A, Strauss LG, Burger C.
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the 6-[18F]fluoro-L-dopa (FDOPA)
kinetics with PET in patients with treated melanoma metastases and to compare it
with the standard tracer 18F-FDG as well as with the perfusion tracer
(15)O-water in selected cases. METHODS: The study included 11 patients (22
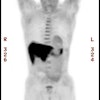
lesions) with pretreated metastatic melanomas. Dynamic studies with FDG and in
selected cases with (15)O-water (eight patients) preceded the FDOPA study. A
one-tissue-compartment model was used for the evaluation of the FDOPA and
(15)O-water studies, and a two-tissue-compartment model and Patlak analysis were
used for the FDG data. A noncompartment model based on chaos theory was used for
calculating fractal dimension, which is a parameter for heterogeneity. RESULTS:
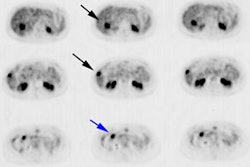
The FDG studies showed a 1.5-fold increased uptake in comparison with
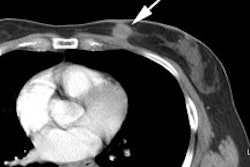
surrounding tissue in 19 of 22 metastatic lesions (sensitivity of 86.4%).
False-negative FDG results were obtained in 2 patients (three lesions). FDOPA
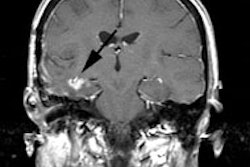
uptake was enhanced in 14 of 22 metastatic lesions (sensitivity of 64%). FDG
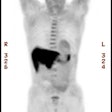
uptake was 1.5-fold higher than FDOPA uptake in 18 of 22 metastases from
melanoma, whereas FDOPA uptake was 1.5-fold higher than FDG uptake in 2 patients
with liver metastases. The data did not show a statistically significant
correlation between the transport constant (K1) for FDOPA and that for FDG or
between the standardized uptake value for FDOPA and FDG in metastases. No
statistically significant correlation was found between K1 for FDOPA and that
for (15)O-water. The data show that FDOPA uptake is not perfusion dependent and
provides different information from FDG. The fractal dimension was similar for
all tracers within the tumor region. Detectability of metastases was enhanced
when both tracers were used (sensitivity of 95%). CONCLUSION: In patients with
negative FDG findings, FDOPA can help to identify viable melanoma metastases and
thus may help to select patients who would benefit from further treatment.