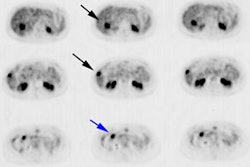
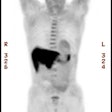
J Am Coll Cardiol 1997 Nov 15;30(6):1451-60
Accuracy of currently available techniques for prediction of functional
recovery after revascularization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction
due to chronic coronary artery disease: comparison of pooled data.
Bax JJ, Wijns W, Cornel JH, Visser FC, Boersma E, Fioretti PM.
OBJECTIVES: This study evaluated the relative merits of the most frequently used
techniques for predicting improvement in regional contractile function after
coronary revascularization in patients with left ventricular dysfunction due to
chronic coronary artery disease. BACKGROUND: Several techniques have been
proposed for predicting improvement in regional contractile function after
revascularization, including thallium-201 (Tl-201) stress-redistribution-reinjection,
Tl-201 rest-redistribution, fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose with positron
emission tomography, technetium-99m sestamibi imaging and low dose dobutamine
echocardiography (LDDE). METHODS: A systematic review of all reports on
prediction of functional recovery after revascularization in patients with
chronic coronary artery disease (published between 1980 and March 1997) revealed
37 with sufficient details for calculating the sensitivity and specificity of
each imaging modality. From the pooled data, 95% and 99% confidence intervals
were also calculated. RESULTS: Sensitivity for predicting regional functional
recovery after revascularization was high for all techniques. The specificity of
both Tl-201 protocols was significantly lower (p < 0.05) and LDDE
significantly higher (p < 0.01) than that of the other techniques.
CONCLUSIONS: Pooled analysis of 37 studies showed that although all techniques
accurately identify segments with improved contractile function after
revascularization, the Tl-201 protocols may overestimate functional recovery.
The evidence available thus far indicates that LDDE appears to have the highest
predictive accuracy.