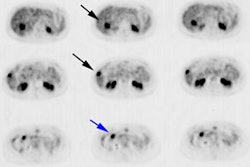
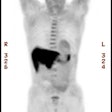
J Clin Oncol 2002 Jan 15;20(2):379-87
Biologic correlates of (18)fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in human breast cancer
measured by positron emission tomography.
Bos R, van Der Hoeven JJ, van Der Wall E, van Der Groep P, van Diest PJ, Comans
EF, Joshi U, Semenza GL, Hoekstra OS, Lammertsma AA, Molthoff CF.
PURPOSE: Variable uptake of the glucose analog (18)fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) has
been noticed in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of breast cancer
patients, with low uptake occurring especially in lobular cancer. At present, no
satisfactory biologic explanation exists for this phenomenon. This study
compared (18)FDG uptake in vivo with biomarkers expected to be involved in the
underlying biologic mechanisms. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Preoperative (18)FDG-PET
scans were performed in 55 patients. (18)FDG activity was assessed visually by
three observers using a four-point score. Tumor sections were stained by
immunohistochemistry for glucose transporter-1 (Glut-1); Hexokinase (HK) I, II,
and III; macrophages; hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alfa (HIF-1alpha); vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF(165)); and microvessels. Mitotic activity index
(MAI), amount of necrosis, number of lymphocytes, and tumor cells/volume were
assessed. RESULTS: There were positive correlations between (18)FDG uptake and
Glut-1 expression (P <.001), MAI (P =.001), amount of necrosis (P =.010),
number of tumor cells/volume (P =.009), expression of HK I (P =.019), number of
lymphocytes (P =.032), and microvessel density (r =.373; P =.005). HIF-1alpha,
VEGF(165), HK II, HK III, and macrophages showed no univariate correlation with
(18)FDG. In logistic regression, however, HIF-1alpha and HK II added value to
MAI and Glut-1. CONCLUSION: (18)FDG uptake in breast cancer is a function of
microvasculature for delivering nutrients, Glut-1 for transportation of (18)FDG
into the cell, HK for entering (18)FDG into glycolysis, number of tumor
cells/volume, proliferation rate (also reflected in necrosis), number of
lymphocytes (not macrophages), and HIF-1alpha for upregulating Glut-1. Together,
these features explain why breast cancers vary in (18)FDG uptake and elucidate
the low uptake in lobular breast cancer.