J Thorac Imaging 1995; bronchiectasis. 10(4):255-267
Aronchick JM, Miller WT Jr
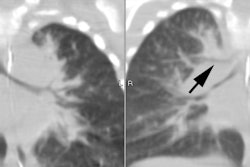
Bronchiectasis is characterized by irreversible dilatation of the airways. Associated with a variety of underlying disorders, the common pathway for the development of bronchiectasis is chronic or recurrent infection. Bronchiectasis can occur in the normal host after a bout of severe infection or bronchial obstruction. Currently, it is more commonly seen in patients with abnormal host defenses including impaired clearance of secretions and disorders of cellular and humoral immunity. Historically, bronchography has been the imaging tool used for the evaluation of bronchiectasis. This procedure has been replaced by high resolution computed tomography, which is currently the modality of choice for imaging patients with bronchiectasis.
PMID: 8523506, MUID: 96105844