J Nucl Med 1994 Jul;35(7):1162-6
Carbon-11-methionine and fluorine-18-FDG PET study in brain hematoma.
Dethy S, Goldman S, Blecic S, Luxen A, Levivier M, Hildebrand J.
Three patients were examined using PET with L-methyl-11C-methionine
(11C-methionine) and 2-18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) 20 to 32 days after
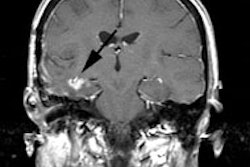
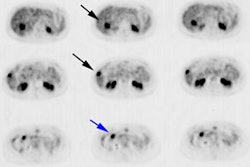
the occurrence of nontumoral brain hematomas. PET revealed high uptake of
11C-methionine in the area surrounding the hematoma in all three patients. In
two patients, discrete spots of moderate uptake of FDG were found at the
periphery of a hypometabolic area. PET studies were repeated in two patients 76
and 103 days after the bleeding, respectively, and showed a dramatic decrease in
11C-methionine uptake around the hematoma. The spots of FDG uptake disappeared
on the repeated late scans. We hypothesize that the subacute gliotic reaction
surrounding brain hematomas is responsible for increased uptake of
11C-methionine and for the presence of spots of FDG uptake. PET studies with
11C-methionine and FDG performed 20 to 32 days after the initial symptom are not
helpful in the differentiation between neoplastic and non-neoplastic origins of
an intracerebral hemorrhage since tracer uptake at the periphery of the lesion
may be increased in both.