Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD):
Clinical:
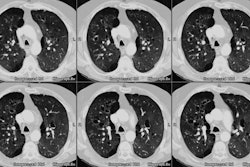
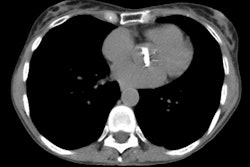
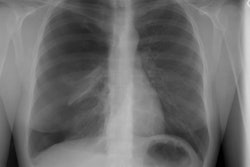
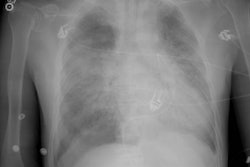
COPD has been defined as a disease state characterized by the presence of airflow obstruction due to chronic bronchitis or emphysema. The airflow obstruction is generally progressive, may be accompanied by airway hyperreactivity, and may be partially reversible [1]. Cigarette smoking is the cause of COPD in 80-90% of cases, but only 10-20% of smokers will develop COPD [1]. Pulmonary function tests reveal a decreased to normal forced vital capacity (the volume of air exhaled from the point of maximum inhalation [TLC or total lung capacity] to maximum exhalation [RV or residual volume]). The forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) to FVC ratio is also decreased (less than 80%). The diffusing capacity of cabon monoxide is also decreased most likely due to loss of pulmonary capillary surface area [1].Patients with severe expiratory airflow limitation due to emphysema (FEV1 less than 0.75 L or 30% of predicted) have a 3 year survival of 50-60% [2]. Patients admitted to the ICU for exacerbation of COPD have a one year mortality rate of 30% irrespective of the need for intubation or mechanical ventilation- in patients over the age of 65 years, the mortality rate at one year doubles [2].
REFERENCES:
(1) Radiol Clin North Am 1998; Stulbarg MS, et al. Obstructive pulmonary disease: The clinicaian's perspective. 36 (1): 1-13
(2) Chest 1999; Gelb AF, et al. Lung function 4 years after lung volume reduction surgery for emphysema. 116: 1608-1615