Radiol Clin North Am 1998 Jan;36(1):15-27
Pathophysiology of obstructive airways disease.
Gurney JW
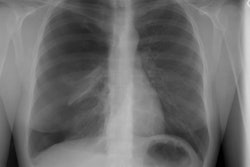
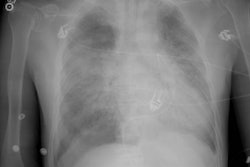
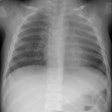
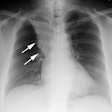
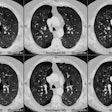
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is a group of disorders that have
in common abnormal airway structure that results in obstruction to airflow.
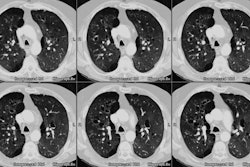
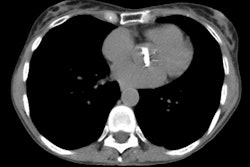
In emphysema, obstruction is thought to be due to the loss of normal elastic
tension in the lung parenchyma. Cigarette smoke is the most important cause
of emphysema. Injurious agents, either in the gas or particulate phase,
incite a proteolytic reaction in the lung. The type of emphysema and its
topographic distribution in the lung stem from normal physiologic processes
that concentrate the cigarette puff both within the lung and within the
secondary pulmonary lobule.