J Nucl Med 2001 Aug;42(8):1166-73
Clinical outcome of patients with previous myocardial infarction and left
ventricular dysfunction assessed with myocardial (99m)Tc-MIBI SPECT and
(18)F-FDG PET.
Zhang X, Liu XJ, Wu Q, Shi R, Gao R, Liu Y, Hu S, Tian Y, Guo S, Fang W.
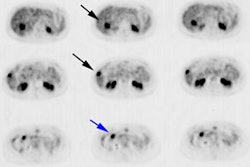
Myocardial viability was assessed by (99m)Tc-methoxyisobutylisonitrile (MIBI)
SPECT and (18)F-FDG PET to evaluate the prognosis and treatment strategy of
patients with myocardial infarction (MI) and left ventricular (LV) dysfunction.
METHODS: One hundred twenty-three consecutive patients with previous MI and LV
dysfunction (LV ejection fraction [EF], 35% +/- 6% [mean +/- SD]) who underwent
(99m)Tc-MIBI SPECT and FDG PET were followed-up for 26 +/- 10 mo (mean +/- SD).
Distributions of the 2 radiotracers in myocardial segments were classified into
2 patterns: myocardial perfusion-metabolism mismatch (MM) and match (M). LV EF
and LV end-diastolic diameter (EDD) were measured by echocardiography at
baseline, 3 mo (Pos1), and 6 mo (Pos2) after revascularization. Cardiac death,
acute MI, unstable angina, and late revascularization (>3 mo) experienced by
the patients during follow-up were defined as cardiac events. RESULTS:
Sixty-seven patients underwent revascularization and 56 patients were treated
medically. Of the 72 patients with > or =2 MM segments, 42 underwent
revascularization (group A1) and 30 were treated medically (group A2). Of the 51
patients with <2 MM segments, 25 underwent revascularization (group B1) and
26 were treated medically (group B2). The 4 groups had similar baseline
characteristics and rest LV EF. After revascularization, EF (mean +/- SD)
increased in group A1 from 36% +/- 5% to 44% +/- 8% (P < 0.0001) in Pos1 and
to 51% +/- 9% (P < 0.0001) in Pos2. EDD (mean +/- SD) decreased from 62 +/- 8
mm to 56 +/- 5 mm (P < 0.001) in Pos1 and to 55 +/- 5 mm (P < 0.001) in
Pos2. However, EF and EDD were unchanged in group B1 (P > 0.05). During the
follow-up, 22 patients (17.9%) suffered from cardiac events, including 11
cardiac deaths, 4 acute MI, 6 late coronary artery bypass grafting, and 1
unstable angina pectoris. The cardiac event rate in group A2 (50%) was
significantly higher than that of groups A1 (2.4%; chi(2) = 23.08; P <
0.0001), B1 (12%; chi(2) = 8.94; P = 0.003), and B2 (11.5%; chi(2) = 9.45; P =
0.002). CONCLUSION: Assessment of myocardial viability using hybrid (99m)Tc-MIBI
SPECT and FDG PET can predict the clinical outcome and is helpful to decision
making in the treatment strategy of patients with MI and LV dysfunction.
Revascularization can improve the LV function and clinical outcome of patients
with >2 viable myocardial segments.