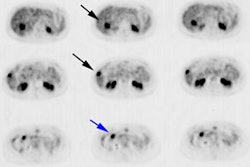
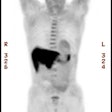
J Nucl Med 2001 Jan;42(1):9-16
Glucose metabolism of breast cancer assessed by 18F-FDG PET: histologic
and immunohistochemical tissue analysis.
Avril N, Menzel M, Dose J, Schelling M, Weber W, Janicke F, Nathrath W, Schwaiger M.
Department of Nuclear Medicine, Technische Universitat Munchen, Munich, Germany.
Breast cancer is characterized by elevated glucose consumption resulting in increased
uptake of 18F-FDG. However, tracer uptake varies considerably among tumors imaged with
PET. This study compared histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis of breast
carcinomas with preoperative FDG uptake assessed by PET to identify tumor characteristics
that define the degree of tracer accumulation. METHODS: FDG uptake in breast tumors was
quantified by calculating standardized uptake values (SUVs) corrected for partial-volume
effect and normalized to blood glucose level at the time of tracer injection. The
histologic sections of 50 invasive and 6 noninvasive breast carcinomas were analyzed for
histologic type, microscopic tumor growth pattern, percentage of tumor cells, presence of
inflammatory cells, density of blood vessels, histopathologic grading, tumor cell
proliferation (mitotic rate and antibody binding of MIB-1), expression of estrogen and
progesterone receptors, and expression of the glucose transporter protein Glut-1. RESULTS:
A positive correlation was found between FDG uptake and histologic tumor type (ductal vs.
lobular; P = 0.003), microscopic tumor growth pattern (nodular vs. diffuse; P = 0.007),
and tumor cell proliferation (MIB-1; P = 0.009). Tumors with diffuse growth patterns had
significantly lower SUVs compared with clearly defined tumors. A weak relationship was
found between FDG uptake and the percentage of tumor cells (P = 0.06). Lower densities of
blood vessels corresponded to higher FDG uptakes (P = 0.08). However, even significant
correlations showed poor correlation coefficients. No relationship was found between FDG
uptake and the following: tumor size; axillary lymph node status; percentage of necrotic,
fibrotic, and cystic compounds; presence of inflammatory cells; steroid receptor status;
and expression of Glut-1. CONCLUSION: Histologic and immunohistochemical tissue analysis
was unable to sufficiently explain the variation of FDG uptake in breast cancer. The
degree of metabolic changes after malignant transformation is most likely explained by a
complex interaction between cellular energy demand and tumoral microenvironment.
Therefore, FDG PET imaging may not be used to estimate tumor biologic behavior of breast
cancer such as differentiation, histopathologic grading, cell proliferation, or axillary
lymph node status.
PMID: 11197987