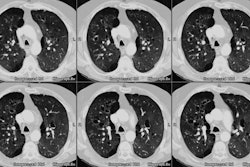
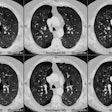
Air trapping on expiratory high-resolution CT scans in the absence of inspiratory scan abnormalities: correlation with pulmonary function tests and differential diagnosis.
Arakawa H, Webb WR
OBJECTIVE: We wish to describe the differential diagnosis and pulmonary function correlates of patients with normal findings on inspiratory high-resolution CT (HRCT) scans who showed air trapping on expiratory scans. MATERIALS AND METHODS: HRCT scans in 273 consecutive patients with suspected diffuse lung disease were reviewed. HRCT consisted of inspiratory scans at 1- to 2-cm intervals and expiratory scans at three levels. Studies considered to show expiratory air trapping were divided into two groups, one having normal findings on inspiratory scans and one having abnormal findings on inspiratory scans. Pulmonary function test results in these groups were compared with a group of patients who had normal findings on inspiratory and expiratory HRCT scans. RESULTS: Forty-five patients showed air trapping on expiratory HRCT scans. Of these 45 patients, inspiratory high-resolution CT scans showed abnormal findings in 36 (bronchiectasis, bronchiolitis obliterans, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and cystic fibrosis). In the remaining nine patients, inspiratory HRCT had normal findings; conditions in these nine patients included bronchiolitis obliterans (n = 5), asthma (n = 3), and chronic bronchitis (n = 1). Results of pulmonary function tests in patients with air trapping and normal findings on inspiratory scans were intermediate, falling between those of patients with normal findings on inspiratory and expiratory HRCT scans and those of patients with air trapping and abnormal findings on inspiratory scans. CONCLUSION: Air trapping on expiratory HRCT scans in patients with normal findings on inspiratory scans is most often associated with bronchiolitis obliterans and asthma. Obtaining expiratory scans in patients who may have one of these diseases is recommended.