| Semin Nucl Med 2000 Oct;30(4):281-298 |
18-Fluorodeoxyglucose imaging with positron emission tomography and single
photon emission computed tomography: cardiac applications.
Bax JJ, Patton JA, Poldermans D, Elhendy A, Sandler MP.
The assessment of myocardial viability has become an important aspect of the diagnostic
and prognostic work-up of patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Although
revascularization may be considered in patients with extensive viable myocardium, patients
with predominantly scar tissue should be treated medically or evaluated for heart
transplantation. Among the many viability tests, noninvasive assessment of cardiac glucose
use (as a marker of viable tissue) with F18-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) is considered the
most accurate technique to detect viable myocardium. Cardiac FDG uptake has traditionally
been imaged with positron emission tomography (PET). Clinical studies have shown that
FDG-PET can accurately identify patients with viable myocardium that are likely to benefit
from revascularization procedures, in terms of improvement of left ventricular (LV)
function, alleviation of heart failure symptoms, and improvement of long-term prognosis.
However, the restricted availability of PET equipment cannot meet the increasing demand
for viability studies. As a consequence, much effort has been invested over the past years
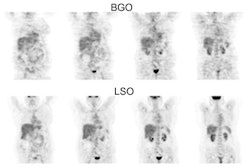
in the development of 511-keV collimators, enabling FDG imaging with single-photon
emission computed tomography (SPECT). Because SPECT cameras are widely available, this
approach may allow a more widespread use of FDG for the assessment of myocardial
viability. Initial studies have directly compared FDG-SPECT with FDG-PET and consistently
reported a good agreement for the assessment of myocardial viability between these 2
techniques. Additional studies have shown that FDG-SPECT can also predict improvement of
LV function and heart failure symptoms after revascularization. Finally, recent
developments, including coincidence imaging and attenuation correction, may further
optimize cardiac FDG imaging (for the assessment of viability) without PET systems.