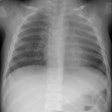
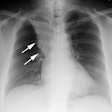
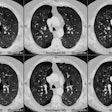
Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification:
Clinical:
The lung is one of the primary sites of metastatic calcification deposition in patients with hypercalcemia. Most affected patients are asymptomatic. The distribution can be diffuse, lobar, or predominantly apical.X-ray:
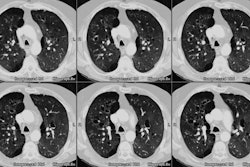
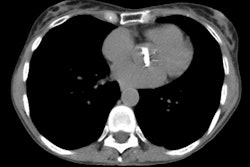
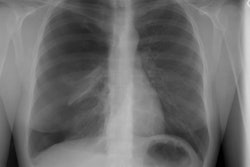
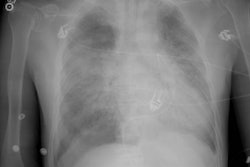
Although pulmonary calcification is found in 60-80% of patients with chronic renal failure at autopsy, plain film radiographs are not very effective in the detection of metastatic pulmonary calcification.. When present the most common finding is numerous ill-defined nodular opacities measuring 3 to 10 mm in size. Calcification within the nodular opacities may not be evident on plain films. Areas of patchy parenchymal opacification are less commonly seen. CT will also demonstrate the nodules, but other findings include areas of ground-glass and patchy consolidation. Calcification is better appreciated by CT. Septal thickening, effusions, and adenopathy are not features of this disorder.REFERENCES:
(1) AJR 1994; Hartman TE, et al. Metastatic
pulmonary calcification in patients with hypercalcemia: Findings on chest
radiographs and CT scans. 162: 799-802