Paratracheal Air Cyst/Tracheal Diverticulum:
Clinical:
A tracheal diverticulum is a rare entity that is thought to be produced by mucosal herniation through a weak point in the tracheal wall as a result of increased intralumenal pressure (such as seen with a chronic cough) [1]. Underlying diseases seen in association with tracheal diverticula include obstructive airway disease, pulmonary TB, and bronchiectasis [1]. Congential tracheal diverticula are also rare and are thought to be related to malformed supernumerary branches of the trachea [1]. Differential considerations include a lymphoepithelial cyst or a bronchogenic cyst with tracheal communication [1].
X-ray:
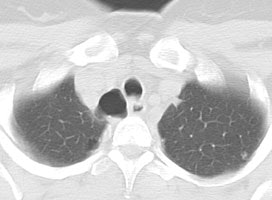
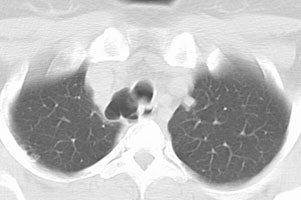
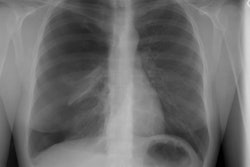
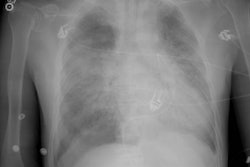
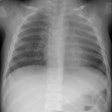
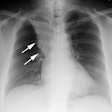
The diverticulum is almost always located to the right posterolateral aspect of the tracheal air column (98%) at the level of the thoracic inlet [1]. The right sided nature of the diverticulum may be related to the fact that the esophagus generally lies to the left of the tracheas at this level, leaving the right side unsupported [1]. Changes in the size of the diverticulum can be seen with respiration [1]. The wall of the cyst can be irregularly thickened in up to one-third of patients [1].
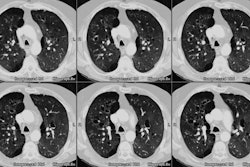
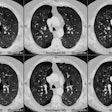
Tracheal diverticulum: The patient shown below was being evaluated for active pulmonary tuberculosis and was incidentally discovered to have a tracheal diverticulum. Note the slightly irregular wall of the diverticulum which can be seen in almost one-third of cases. Click here to view cine image which nicely confirms communication with the trachea. |
|
REFERENCES:
(1) AJR 1999; Goo JM, et al. Right paratracheal air cysts in the thoracic inlet: Clinical and radiologic significance. 173: 65-70