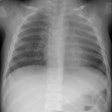
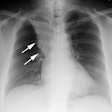
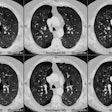
Advanced emphysema: preoperative chest radiographic findings as predictors of outcome following lung volume reduction surgery.
Maki DD, Miller WT Jr, Aronchick JM, Gefter WB, Miller WT Sr, Kotloff RM, Tino G
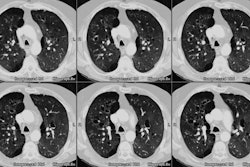
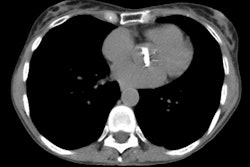
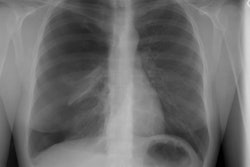
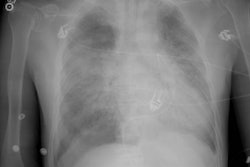
PURPOSE: To determine whether preoperative chest radiographic findings alone can reliably predict which patients will achieve the best functional outcome of lung volume reduction surgery. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The preoperative chest radiographs obtained in 57 patients who had undergone lung volume reduction surgery were retrospectively scored by five blinded readers for severity and distribution of emphysema, evidence of lung compression, disease heterogeneity, and other features. Comparisons were made with the 3-6-month postoperative functional outcome for each patient. RESULTS: High disease heterogeneity (score > 2) and unequivocal lung compression (score 1) both were 100% predictive of a favorable outcome (FEV1 increase, > or = 30%). Low heterogeneity (score < 1) was 94% predictive of an unfavorable outcome (FEV1 increase < 30%), as was a lack of lung compression, which was 92% predictive of an unfavorable outcome. These two features also correlated with an improved 6-minute walk test result, although this correlation was weaker. CONCLUSION: Chest radiography alone may be sufficient for initial screening. High disease heterogeneity and lung compression on chest radiographs are highly predictive of a favorable functional outcome.
Comments:
Comment in: Radiology 1999 Jul;212(1):1-3