Bronchiolitis obliterans. Report of three cases with detailed physiologic studies.
Seggev JS, Mason UG 3d, Worthen S, Stanford RE, Fernandez E
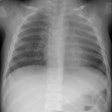
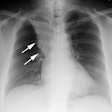
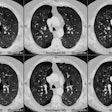
We describe three patients with bronchiolitis obliterans seen at our hospital during the last two years. Their ages were 25, 49 and 69 years. One developed the disease secondary to a probable viral infection, another inhaled fumes, and the third was exposed to unknown precipitating factors. Lung biopsy showed changes compatible with bronchiolitis obliterans in the first two, while in the third, changes were compatible with bronchiolitis obliterans and interstitial pneumonitis. Pulmonary function tests of patient 1 showed severe airflow limitation, increased total lung capacity, a shift of the pressure-volume curve upward with a normal slope, and an elevation of upstream resistance. In patient 3 (bronchiolitis obliterans with interstitial pneumonitis) total lung capacity was normal, the pressure volume curve was shifted slightly to the right and upstream resistance was increased. After treatment with steroids, clinical improvement was observed along with normalization of the pressure-volume curve and a decline in the upstream resistance.