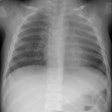
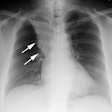
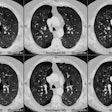
Radiology 1998 Jul;208(1):193-9
Ventilator-associated pneumonia in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome: CT evaluation.
Winer-Muram HT, Steiner RM, Gurney JW, Shah R, Jennings SG, Arheart KL, Eltorky MA, Meduri GU
PURPOSE: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of computed tomography
(CT) for pneumonia in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS). MATERIALS AND METHODS: CT scans were obtained within 1 week of
bronchoscopic sampling in 31 patients receiving mechanical ventilation
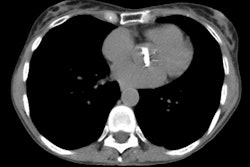
for ARDS for more than 48 hours. Of 11 patients with pneumonia, five developed
symptoms less than 11 days after the onset of ARDS (early ARDS). CT scans
were rated for pneumonia independently by four radiologists who were unaware
of the clinical diagnosis. Diagnostic accuracy was defined by means of
the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, or A2. RESULTS:
Diagnostic accuracy for pneumonia was fair (A2 = 0.69 +/- 0.04 [standard
error]) owing to 70% true-negative ratings (vs 59% true-positive ratings).
The generalizability coefficient was good (0.79). No single CT finding
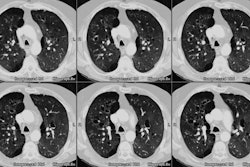
was significantly different for the presence of pneumonia. Nondependent
opacities predominated in 10 (91%) of 11 patients with pneumonia and 12
(60%) of 20 without pneumonia. Nondependent opacities predominated in nine
(56%) of 16 patients with early ARDS and 13 (87%) of 15 with late ARDS.
CONCLUSION: CT has fair diagnostic accuracy for ventilator-associated pneumonia
in patients with ARDS owing primarily to identification of patients without
pneumonia. No single CT sign was significantly different for pneumonia,
but dependent atelectasis was more common in patients with early ARDS without
pneumonia.