Radiology 1996 Aug;200(2):349-356
Opportunistic bronchopulmonary infections after lung transplantation: clinical and radiographic findings.
Shreeniwas R, Schulman LL, Berkmen YM, McGregor CC, Austin JH
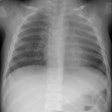
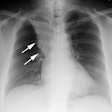
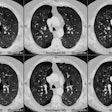
PURPOSE: To assess clinical and radiographic findings in opportunistic bronchopulmonary infections after lung transplantation. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Forty-five episodes of opportunistic bronchopulmonary infection occurred in 27 (35%) of 77 lung transplant recipients during a 4-year period. Causative organisms, radiographic patterns, and mortality were reviewed. RESULTS: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) was the most common pathogen (25 episodes), followed by Aspergillus species (seven episodes), Pneumocystis carinii (six episodes), herpes simplex virus (four episodes), Mycobacterium avium complex (two episodes), and M tuberculosis (one episode). Eighteen of the 25 episodes (72%) of CMV pneumonitis occurred in the first 4 months after transplantation; 24 (96%) occurred within the 1st year. Radiographic patterns of symptomatic CMV pneumonitis were diffuse haziness (60%), focal haziness (33%), and focal consolidation (7%). Aspergillus species locally invaded a necrotic bronchial anastomosis in three patients, each within 4 months of transplantation. P carinii was seen as focal haziness and caused no symptoms. Radiographic findings, when present, were seen almost exclusively in the transplanted lung. Despite three deaths attributable to opportunistic bronchopulmonary infection, the difference between the survival rates of patients with and those of patients without bronchopulmonary infection was not statistically significant (82% and 81%, respectively, 1 year after transplantation). CONCLUSION: Opportunistic bronchopulmonary infections are common after lung transplantation. The most common pathogen is CMV, which causes diverse chest radiographic patterns. Opportunistic bronchopulmonary infections do not adversely affect overall mortality.
PMID: 8685324, MUID: 96294566