J Nucl Med 2002 Feb;43(2):167-72
Comparison of (11)C-choline and (18)F-FDG PET in primary diagnosis and
staging of patients with thoracic cancer.
Pieterman RM, Que TH, Elsinga PH, Pruim J, van Putten JW, Willemsen AT, Vaalburg
W, Groen HJ.
PET with (18)F-FDG is used for detection and staging of thoracic cancer;
however, more specific PET radiopharmaceuticals would be welcome. (11)C-labeled
choline (CHOL) is a new radiopharmaceutical potentially useful for tumor
imaging, since it is incorporated into cell membranes as phosphatidylcholine.
The aim of this study was to investigate whether (11)C-CHOL PET has advantages
over (18)F-FDG PET in patients with thoracic cancer. METHODS: We evaluated 17
patients with thoracic cancer both with (11)C-CHOL PET and (18)F-FDG PET. After
transmission scanning, (11)C-CHOL was injected intravenously, and whole-body
scanning was started after 5 min. Immediately thereafter, (18)F-FDG was injected
intravenously, followed after 90 min by interleaved attenuation-corrected
whole-body scanning. Scans were performed from crown to femur. Visual and
quantitative (standardized uptake value) analyses of (11)C-CHOL PET and
(18)F-FDG PET were performed and compared with results of traditional staging
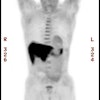
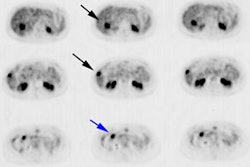
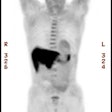
and follow-up. RESULTS: The most prominent features of normal (11)C-CHOL
distribution were high uptake in liver, renal cortex, and salivary glands.
Except for some uptake in choroid plexus and pituitary gland, brain uptake was
negligible. All primary thoracic tumors were detected with (11)C-CHOL PET and
(18)F-FDG PET. Both (11)C-CHOL PET and (18)F-FDG PET correctly identified all 16
patients with lymph node involvement. However, in a lesion-to-lesion analysis,
(11)C-CHOL PET detected only 29 of 43 metastatic lymph nodes, whereas (18)F-FDG
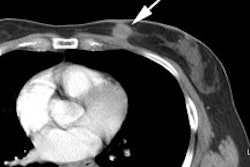
PET detected 41 of 43. (11)C-CHOL PET detected fewer intrapulmonary and pleural
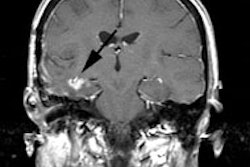
metastases than (18)F-FDG PET (27/47 vs. 46/47). More brain metastases were
detected with (11)C-CHOL PET (23/23) than with (18)F-FDG PET (3/23). For primary
tumors, the median (range) standard uptake values of (11)C-CHOL and (18)F-FDG
were 1.68 (0.98-3.22) and 4.22 (1.40-8.26), respectively (P = 0.001).
CONCLUSION: (11)C-CHOL PET can be used to visualize thoracic cancers. Although
detection of lymph node metastases with (11)C-CHOL PET was inferior compared
with (18)F-FDG PET, the detection of brain metastases was superior.