| J Nucl Med 1995 Nov;36(11):2110-2119 |
Rest myocardial perfusion/metabolism imaging using simultaneous
dual-isotope acquisition SPECT with technetium-99m-MIBI/fluorine-18-FDG.
Delbeke D, Videlefsky S, Patton JA, Campbell MG, Martin WH, Ohana I, Sandler MP.
The purpose of this study was to develop a dual-isotope simultaneous acquisition (DISA)
protocol using a multihead SPECT camera equipped with an ultrahigh-energy (UHE) collimator
to evaluate simultaneously rest cardiac perfusion and metabolism with 99mTc-MIBI/18FDG.
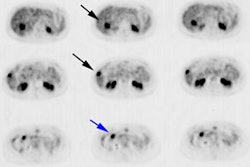
METHODS: Physical measurements were first performed with phantoms to develop the
acquisition protocol. Fifteen patients underwent DISA-SPECT with 99mTc-MIBI/18FDG to
validate the protocol. To evaluate the quality of the 99mTc-MIBI images acquired with the
UHE collimator, four patients underwent a resting 99mTc-MIBI scan acquired with a
high-resolution, low-energy collimator prior to DISA-SPECT. RESULTS: With a window of 20%
for both photopeaks and a 99mTc/18F concentration ratio of 3.2:1, the spillover from 18F
into the 99mTc window is 6% of the counts in the window for normal subjects. Phantom
images clearly demonstrated defects measuring 2 x 1 and 2 x 0.5 cm. Technetium-99m-MIBI
images obtained with the UHE and high-resolution collimators provided similar diagnostic
information. Using a stenosis of > 70% as criteria to diagnose coronary artery disease,
DISA-SPECT had a sensitivity of 100% and a positive predictive value of 93%. CONCLUSION:
Simultaneous evaluation of rest myocardial perfusion/metabolism with a multihead SPECT
camera equipped with an UHE collimator is possible using 99mTc-MIBI/18FDG with a
dual-isotope simultaneous acquisition protocol.