Bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation: high-resolution CT findings in 15 patients.
Worthy SA, Park CS, Kim JS, Muller NL
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study was to compare the high-resolution
CT findings in patients with pathologically
proven bronchiolitis obliterans after lung transplantation with high-resolution
CT findings in control subjects. MATERIALS
AND METHODS: High-resolution CT examinations of 15 patients with pathologically
proven bronchiolitis obliterans after
lung transplantation and 18 control subjects were retrospectively evaluated
by two independent observers who were
unaware of the diagnosis in each case. All 33 subjects underwent inspiratory
high-resolution CT. Five patients with
bronchiolitis obliterans and 16 control subjects underwent expiratory
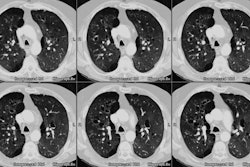
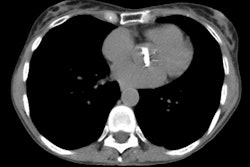
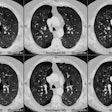
CT. RESULTS: Findings in patients with bronchiolitis
obliterans included bronchial dilatation in 80%, mosaic perfusion in
40%, bronchial wall thickening in 27%, and air
trapping in 80%, compared with the control subjects with bronchial
dilatation in 22%, mosaic perfusion in 22%, and air
trapping in 6%. The combination of bronchial dilatation on the inspiratory
CT scan and air trapping on the expiratory CT
scan was seen only in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans. We calculated
good agreement between the two observers
(kappa > or = .63). CONCLUSION: Air trapping and bronchial dilatation
were the two most sensitive and specific findings
on high-resolution CT scans of patients with bronchiolitis obliterans.
The combination of these two findings was seen
exclusively in patients with bronchiolitis obliterans.