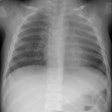
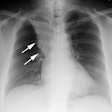
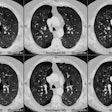
Radiology 2001 Mar;218(3):689-93
Acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by pulmonary and
extrapulmonary injury: a comparative ct study.
Desai SR, Wells AU, Suntharalingam G, Rubens MB, Evans TW, Hansell DM.
PURPOSE: To determine computed tomographic (CT) differences between acute respiratory
distress syndrome (ARDS) due to pulmonary injury (ARDS(p)) and extrapulmonary injury
(ARDS(ex)). MATERIALS AND METHODS: CT appearances in 41 patients (27 male, 14 female; mean
age, 47.1 years +/- 17.1 [SD]; age range, 17-79 years; those with ARDS(p), n = 16; those
with ARDS(ex), n = 25) were categorized as typical or atypical of ARDS by two observers.
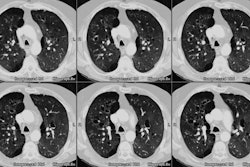
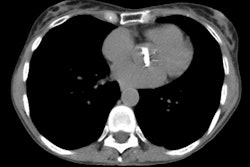
The extent of individual CT patterns was also quantified. RESULTS: Typical CT appearances
were more frequent in ARDS(ex) than ARDS(p) (18 [72%] of 25 vs five [31%] of 16 patients,
respectively; P: <.01). Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of a typical CT pattern
for the diagnosis of ARDS(ex) were 72%, 69%, and 71%, respectively. Atypical appearances
were characterized by more extensive nondependent intense parenchymal opacification (IPO)
(P: =.03) and cysts (P: =.05), whereas typical CT appearances had more extensive dependent
IPO (P: =.01). Typical appearances at CT were independently related to the cause of ARDS
(odds ratio, 8.9; 95% CI: 1.8, 44.2; P: <.01) but were independent of the time from
intubation. Foci of nondependent IPO were more extensive in ARDS(p) (P: =.05) than
ARDS(ex), but this finding was ascribable to differences in time to CT (after intubation)
between ARDS(p) and ARDS(ex). CONCLUSION: The differentiation between ARDS(p) and ARDS(ex)
can, with some caveats, be based on whether the CT appearances are typical or atypical of
ARDS but not on any individual CT pattern in isolation.
PMID: 11230641