Radiology 1999 Sep;212(3):803-9
Staging non-small cell lung cancer with whole-body PET.
Marom EM, McAdams HP, Erasmus JJ, Goodman PC, Culhane DK, Coleman RE, Herndon JE,
Patz EF Jr.
PURPOSE: To compare the accuracies of whole-body 2-[fluorine
18]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET) and
conventional imaging (thoracic computed tomography [CT], bone scintigraphy, and
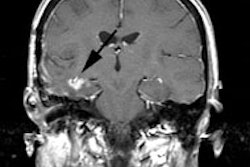
brain CT or magnetic resonance [MR] imaging) in staging bronchogenic carcinoma.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: Within 20 months, 100 patients with newly diagnosed
bronchogenic carcinoma underwent whole-body FDG PET and chest CT. Ninety of
these patients underwent radionuclide bone scintigraphy, and 70 patients
underwent brain CT or MR imaging. For each patient, all examinations were
completed within 1 month. A radiologic stage was assigned by using PET and
conventional imaging independently and was compared with the pathologic stage.
The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and negative and positive predictive
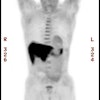
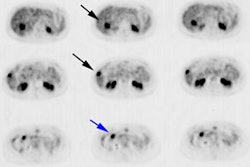
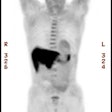
values were calculated. RESULTS: PET staging was accurate in 83 (83%) patients;
conventional imaging staging was accurate in 65 (65%) patients (P < .005).
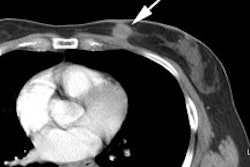
Staging with mediastinal lymph nodes was correct by using PET in 67 (85%)
patients and by using CT in 46 (58%) patients (P < .001). Nine (9%) patients
had metastases demonstrated by using PET that were not found with conventional
imaging, whereas 10 (10%) patients suspected of having metastases because of
conventional imaging findings were correctly shown with PET to not have
metastases. CONCLUSION: Whole-body PET was more accurate than thoracic CT, bone
scintigraphy, and brain CT or MR imaging in staging bronchogenic carcinoma.