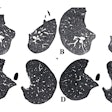
An automated software application for determining liver volume on CT images can yield dramatic time savings over manual volumetry techniques when planning liver transplants by reducing variation among radiologists, according to an article in the October issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology.
University of Chicago researchers found that their automated CT volumetry software could assess liver volumes in about four minutes, compared with approximately 40 minutes per case for the manual method. Automated results also demonstrated excellent agreement with manual volumetry.
"With our system, fairly accurate liver volumetry can be done in a very short time," lead author Kenji Suzuki, PhD, told AuntMinnie.com.
Evaluating liver volume is crucial in liver transplant planning because appropriate graft size is one of the major predictors of a safe, successful outcome for both the donor and recipient. While manual tracing -- the current gold standard -- provides accurate results, it's very time-consuming and subjective, Suzuki said. As a result, the research team sought to develop a software-based automated liver volumetry technique.
The algorithm has four steps. First, a 3D anisotropic diffusion filter is applied to the original hepatic CT volume to remove noise while preserving liver structures. Next, a 3D scale-specific gradient magnitude filter enhances the liver boundary. Liver extraction is then performed via 3D geodesic active contour segmentation with a level-set algorithm, according to the researchers. Finally, the software calculates the liver volume (AJR, October 2011, Vol. 197:4, pp. W706-W712).
The team tested the software on hepatic CT scans from 18 consecutive registered prospective liver donors from May 2006 to January 2008. There were 10 women and eight men with a mean age of 33.1 ± 10.3 years (range, 20-52 years).
CT scans were obtained under a liver transplant protocol on a Brilliance CT scanner (Philips Healthcare) and using Omnipaque nonionic contrast (GE Healthcare). An abdominal radiologist with 10 years of experience performed interactive volumetry using Volume Tracing in Advanced Vessel Analysis software (Philips) on an Extended Brilliance Workspace v3.0.1.3200 viewing workstation (Philips).
An abdominal radiologist with 15 years of experience specializing in liver imaging also manually traced the liver contour on each CT slice to establish a reference standard.
Accuracy of manual versus automated liver volumetry
|
While both interactive and automated volumetry demonstrated excellent agreement with the manual method (intraclass correlation coefficients of 0.96 and 0.94, respectively), automated volumetry had a statistically significant improvement (p < 0.05) in average user time per case over the other two methods.
"Therefore, automated volumetry is an efficient, accurate, useful way of measuring liver volume at CT," the authors wrote.
The researchers plan to utilize the automated liver extraction method created for this study as a key component in a computer-aided detection (CAD) system they're developing, Suzuki said.
"We plan to expand our total liver volumetry system to include automated volumetry of segmental liver volumes," according to Suzuki. "Also, we plan to keep improving the performance of our automated CT volumetry system, because there are still occasional false positives which need manual removal [although this can be accomplished rapidly with routine manipulations]."