Tuesday, November 27 | 12:15 p.m.-12:45 p.m. | NR397-SD-TUA7 | Lakeside, NR Community, Station 7
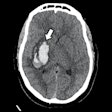
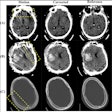
Researchers from the Netherlands have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) algorithm capable of segmenting brain vasculature on 4D CT angiography (CTA) scans, according to this Tuesday poster presentation.Segmenting the entire brain vasculature is an essential part of evaluating the brain with 4D CTA, presenter Midas Meijs, a doctoral candidate at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, told AuntMinnie.com.
Seeking to automate this task, Meijs and colleagues trained and tested a convolutional neural network, U-Net, on the 4D CTA scans of 162 patients suspected of having had a stroke. U-Net took into account both temporal and spatial features from the 4D imaging data.
The automated deep-learning algorithm was able to segment the complete brain vasculature on 4D CTA scans with high accuracy, regardless of the size of individual blood vessels, the group found. Furthermore, the algorithm processed the full 4D CTA dataset in less than 90 seconds.
Using an AI algorithm to assist in the segmentation of cerebral vasculature may improve visualization of the brain and ultimately help clinicians assess brain blood flow and detect potential pathology, Meijs said.
"Automated segmentation in 4D CTA is an important step toward the automated localization and evaluation of vascular pathology," he said.