Wednesday, December 4 | 3:40 p.m.-3:50 p.m. | SSM14-05 | Room E353C
In this scientific session, researchers from Massachusetts will describe how generative adversarial networks (GANs) can be utilized to predict survival in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF).Due to the condition's poor prognosis, accurate prediction of disease progression and mortality is crucial for optimal therapeutic decision-making and management of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis -- the most common progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease, according to senior study author Hiroyuki Yoshida, PhD, of Harvard Medical School in Boston.
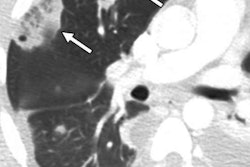
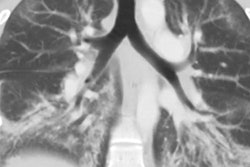
"However, the disease course of IPF is highly heterogeneous and cannot accurately be predicted for individual patients," he told AuntMinnie.com. "Although quantitative CT imaging is becoming a promising prognostic biomarker for IPF, currently none of the existing biomarkers have come to the forefront for common clinical use."
As a result, the team of researchers developed pix2surv, a GAN-based artificial intelligence (AI) model that can automatically predict the mortality of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis directly from chest CT images. From testing, they found that pix2surv yielded superior performance to existing clinical, physiological, and quantitative CT imaging biomarkers for predicting mortality.
"Therefore, our GAN-based survival model is a promising approach for substantially improving the current state of the art in the prediction of mortality in patients with IPF," Yoshida said. "Such schemes will enable optimal therapeutic decision-making and highly accurate management of patients with IPF."
Check out this Wednesday afternoon presentation to get all the details.