Wednesday, December 4 | 11:00 a.m.-11:10 a.m. | SSK05-04 | Room N229
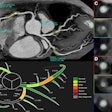
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) scoring should be integrated into CT lung cancer screening exams, according to researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital.The presence of coronary artery calcification on CT scans is an important finding because of the implications it can have on diagnosing coronary artery disease and subsequent therapeutic interventions. CT lung screening may offer an opportunity for clinicians to obtain CAC scores of individuals without undergoing an additional exam.
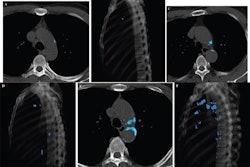
Exploring this idea, the researchers investigated the significance of CAC incidentally detected on the CT lung screening exams of 3,110 individuals who underwent screening at their institution between January 2016 and September 2018.
The group discovered that nearly a quarter of the study participants had significant coronary artery calcification. Among these individuals, calcification led to changes in management for roughly 20%.
"We found that when significant coronary artery calcification is reported on lung cancer screening CTs, referring physicians frequently change the management of their patients, particularly in those without established coronary artery disease," Dr. Dexter Mendoza told AuntMinnie.com.
Management changes most often involved changes in medication regimen, followed by further diagnostic testing, referrals to a cardiology specialist, and invasive interventions such as coronary artery stenting.
"We recommend that radiologists routinely report the presence and degree of coronary artery calcification seen on lung cancer screening CTs," Mendoza said.