Vaccines are effective for reducing the severity of the omicron variant of COVID-19, according to a study published March 7 in Radiology.
The findings "emphasize the need for good vaccine coverage and for the booster dose even with the omicron variant," wrote a team led by Dr. Amandine Crombé of Imadis, an x-ray laboratory in Lyon, France.
"Our results confirm that both the omicron variant and vaccination were associated with lower frequency of typical chest CT for COVID-19 and lesser extent of disease, with higher number of vaccine doses showing an increasing protective impact against high severity score, which emphasizes the benefit of the booster dose," the group noted.
The omicron variant of COVID-19 is more communicable but tends to be less severe compared to other variants, the team noted. But there's not much research on how omicron and a patient's vaccination status affect chest CT findings.
Crombé and colleagues sought to explore the question via a study that included 3,876 patients who presented at 93 emergency departments between July 2021 and March 2022 with either omicron or delta variants of COVID-19 (diagnosed with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction [RT-PCR] testing) and with known vaccination status; patients also underwent CT imaging. The investigators tracked disease severity for each variant, dividing results into "delta-predominant," "transition," and "omicron-predominant" periods.
The team found the omicron variant to have less typical findings -- and thus, less disease severity -- than the delta variant on chest CT, with an odds ratio for this of 0.46 (with 1 as reference). Two and three vaccine doses were associated with lower odds of demonstrating more severe CT findings, with odds ratios of 0.32 for two vaccine doses and 0.2 for three.
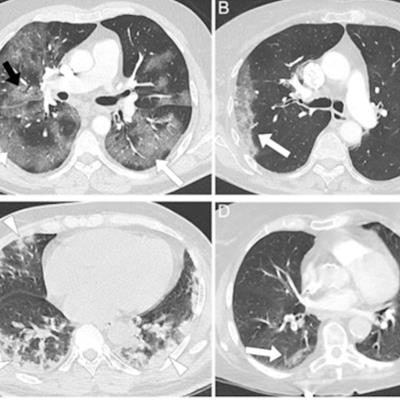
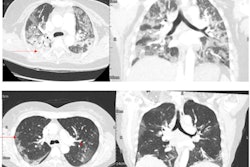
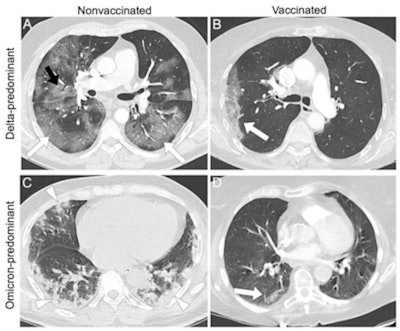 Representative examples of patients with different vaccine statuses during the delta-predominant and omicron-predominant periods. (A) Axial CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA, with lung kernel) of a 65-year-old, nonvaccinated, male patient during the delta-predominant period showing typical CT for COVID-19, i.e., bilateral and asymmetric ground glass opacities (GGOs, white arrows) affecting the central and peripheral lung, associated with reticulations (black arrow) responsible for the 'crazy paving' aspect. The severity score assessed on the entire CTPA was 'severe' extent. (B) Axial CTPA in 57 years old vaccinated male patient (2 doses) during the delta-predominant period showing a "compatible" chest CT for COVID-19, i.e., single unilateral peripheral GGO (white arrow), with a "minimal" severity score. (C) Axial chest CT without contrast medium injection in a 69-year-old nonvaccinated male patient during the omicron predominant showing peripheral, bilateral, and asymmetric consolidations (white arrowhead), classified as 'compatible' with COVID-19. The severity score on the entire chest CT was "extended." (D) Axial CTPA in a 70-year-old vaccinated female patient (3 doses) showing a single small peripheral lesion combining GGO and consolidation (white arrow) classified as "indeterminate" with a "minimal" severity score. Images and caption courtesy of Radiology.
Representative examples of patients with different vaccine statuses during the delta-predominant and omicron-predominant periods. (A) Axial CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA, with lung kernel) of a 65-year-old, nonvaccinated, male patient during the delta-predominant period showing typical CT for COVID-19, i.e., bilateral and asymmetric ground glass opacities (GGOs, white arrows) affecting the central and peripheral lung, associated with reticulations (black arrow) responsible for the 'crazy paving' aspect. The severity score assessed on the entire CTPA was 'severe' extent. (B) Axial CTPA in 57 years old vaccinated male patient (2 doses) during the delta-predominant period showing a "compatible" chest CT for COVID-19, i.e., single unilateral peripheral GGO (white arrow), with a "minimal" severity score. (C) Axial chest CT without contrast medium injection in a 69-year-old nonvaccinated male patient during the omicron predominant showing peripheral, bilateral, and asymmetric consolidations (white arrowhead), classified as 'compatible' with COVID-19. The severity score on the entire chest CT was "extended." (D) Axial CTPA in a 70-year-old vaccinated female patient (3 doses) showing a single small peripheral lesion combining GGO and consolidation (white arrow) classified as "indeterminate" with a "minimal" severity score. Images and caption courtesy of Radiology.The study results underscore the need for radiologists to track the "influence of vaccination and novel variants on CT findings and adapt their interpretations and conclusions accordingly, especially since full vaccination coverage is increasing and new omicron subvariants can reinfect previously immunized individuals," Crombe's team concluded.
The study provides "more robust evidence on the independent associations of vaccination and Omicron with the CT manifestations," wrote Dr. Soon Ho Yoon, PhD, and colleague Dr. Jin Mo Goo, PhD, both of Seoul National University Hospital in South Korea in an accompanying editorial.
"If these findings are validated in a larger population with a longer interval since vaccination, it would provide additional evidence to overcome vaccine hesitancy by demonstrating prolonged vaccine effectiveness against pneumonia," Yoon and Goo noted.












![Images show the pectoralis muscles of a healthy male individual who never smoked (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; body mass index [BMI, calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared], 28.4; number of cigarette pack-years, 0; forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1], 97.6% predicted; FEV1: forced vital capacity [FVC] ratio, 0.71; pectoralis muscle area [PMA], 59.4 cm2; pectoralis muscle volume [PMV], 764 cm3) and a male individual with a smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) (age, 66 years; height, 178 cm; BMI, 27.5; number of cigarette pack-years, 43.2, FEV1, 48% predicted; FEV1:FVC, 0.56; PMA, 35 cm2; PMV, 480.8 cm3) from the Canadian Cohort Obstructive Lung Disease (i.e., CanCOLD) study. The CT image is shown in the axial plane. The PMV is automatically extracted using the developed deep learning model and overlayed onto the lungs for visual clarity.](https://img.auntminnie.com/mindful/smg/workspaces/default/uploads/2026/03/genkin.25LqljVF0y.jpg?auto=format%2Ccompress&crop=focalpoint&fit=crop&h=112&q=70&w=112)