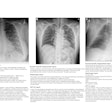
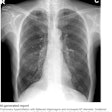
Dual-energy subtraction is a digital radiography (DR) technique in which images are acquired at two x-ray energies, typically one at a high peak kilovoltage and another at a low peak kilovoltage. After postprocessing, two images are produced, one a high-energy soft-tissue image in which overlying bones are removed, and the other a low-energy image that optimally displays bone and calcified thoracic structures.
The researchers have found that detection of calcified cardiovascular pathology is improved on the low-energy bone image. The poster will demonstrate multiple examples of such pathology, such as coronary artery disease, cardiac valvular pathology, and pericardial disease.
The authors believe that many of these pathologies are either undiagnosed or underestimated with conventional chest radiography, and they plan to correlate images with CT and ultrasound to confirm the findings.