Since its acquisition of Bayer Pharma's molecular imaging agent portfolio five months ago, Piramal Imaging has been making steady progress in advancing its PET tracer designed to detect beta-amyloid deposits in the brain, which have been linked to early signs of Alzheimer's disease.
Preliminary results of a phase III clinical trial show that PET with florbetaben can detect beta-amyloid deposits in various regions of the brain in comparison with postmortem analysis of brain tissue. Florbetaben PET achieved 100% sensitivity and 92% specificity with high interreader agreement.
Berlin-based Piramal Imaging, a subsidiary of Indian healthcare conglomerate Piramal Healthcare, began operations on April 1 and currently has offices in Boston and Mumbai, India.
"When Bayer made this very conscious decision to take out the [molecular] imaging business, it was because, first of all, they wanted to focus on therapy and, second, [Bayer] also saw the way to develop imaging agents is very different from therapeutics," recalled Dr. Ludger Dinkelborg, CEO of Piramal Imaging and former head of research for imaging at Bayer.
Therefore, when Bayer made the decision to find a strategic investor, Piramal Healthcare came to the forefront.
Company creation
Piramal Healthcare previously owned and operated a portfolio of branded generic products, which covered therapeutic markets, such as antibiotics, respiratory, cardiovascular, pain, and neuroscience. In September 2010, Piramal Healthcare sold its Healthcare Solutions business to Abbott for $3.8 billion dollars.
Through the Bayer transaction, Piramal Healthcare acquired all of Bayer's intellectual property and was allowed to hire researchers from Bayer's nuclear medicine business unit, as well as staff from chemistry, manufacturing, and other related areas.
"We also have some clinical and regulatory personnel, but we still have openings, because we also want to get some people from the entrepreneurial setting," Dinkelborg said. "Bayer was very helpful, because if this new company is successful, Bayer will benefit financially as well."
Piramal Imaging currently has approximately 25 employees, and the company expects that number to increase quickly. Just last month, Piramal Imaging signed an agreement with radiopharmaceutical provider IBA Molecular (IBA) for IBA to manufacture and distribute florbetaben in European and U.S. markets.
Florbetaben studies
Florbetaben is a PET radiopharmaceutical designed to bind to beta-amyloid clusters in the brain. Beta amyloid has been linked to the development of Alzheimer's disease and other neurologic conditions. A PET scan would detect the uptake of florbetaben as it attaches to beta-amyloid plaques to identify its presence in various brain regions.
 |
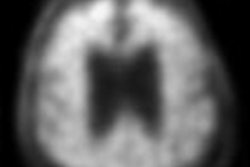
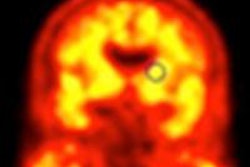
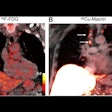
| Axial florbetaben brain PET images (top) and co-registered PET/T1-weighted MRI (bottom), each of a typical Alzheimer's disease patient (A) and a typical healthy control (B). Axial slices are at the level of the basal ganglia. PET images are 90 to 110 minutes after injection; standardized uptake value ratio (SUVR) data are with the cerebellar cortex as the reference region. Image courtesy of Piramal Imaging. |
According to Piramal Imaging, initial studies of florbetaben have shown that it can be administered intravenously in very small doses. Its rapid evacuation from a patient's body and the low dose injected (due to its relatively short half-life of 110 minutes) would make the tracer suitable for clinical use.
Piramal Imaging's current phase III clinical study includes 17 sites on four continents: Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. Part of the trial includes the evaluation of six different brain regions to determine the local presence of beta-amyloid deposits and whether the brain is positive or negative in these areas, such as the hippocampus.
Along with florbetaben-PET images, researchers followed up with MRI exams to correlate the results. To determine which areas of the brain were positive or negative for beta-amyloid deposits, researchers conducted blinded reads on all six regions and obtained images of each brain for pathologists to measure the activity of the beta-amyloid protein.
"We are the only ones who have regional data on both the quantity and the localization of beta amyloid in the brain, plus the correlating images," Dinkelborg said. "That was the main objective in this phase III trial -- to show that, on a regional basis, the beta-amyloid protein measured after autopsy or histological chemistry correlates to the uptake of the tracer in the in vivo image."
Alzheimer's progression
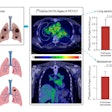
At this year's annual meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, researchers from the Centre for PET at Austin Health in Melbourne, Australia, and Bayer Healthcare presented the results of a study using florbetaben-PET imaging and MRI on 45 subjects with mild cognitive impairment.
Comparing initial images with results at 24-month follow-up, progression to Alzheimer's disease occurred in 75% of mild cognitive impaired subjects with high florbetaben uptake, compared with 53% of mild cognitive impaired participants with hippocampal atrophy.
In addition, 80% of mild cognitive impaired subjects with both high florbetaben uptake and hippocampal atrophy progressed to Alzheimer's, while 19% of subjects with low florbetaben and mild cognitive impairment developed other dementias.
The researchers' conclusion was that high florbetaben binding indicated a "very high risk of progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer's within two years and was a stronger and more specific risk factor than hippocampal atrophy in this cohort."
FDA submission
Piramal Imaging plans to submit its findings on florbetaben to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) before the end of this year.
In the meantime, the company will continue to add patients to the clinical trial. "Because we are the only ones who have this regional assessment, it is very important to continue to work on it," Dinkelborg added.
In addition to florbetaben, Piramal Imaging has seven other clinical compounds that have passed phase I trials. Among the potential products are two amino acids designed to detect tumor metabolism.
"The amino acids are designed not to enter the brain, as FDG would, but only show metastases, which makes them much more specific and better to differentiate between inflammation and tumor," Dinkelborg explained.
The company also has three compounds that have shown promise for prostate cancer. Researchers currently are comparing preliminary data and a decision on which compound to develop has not been made.